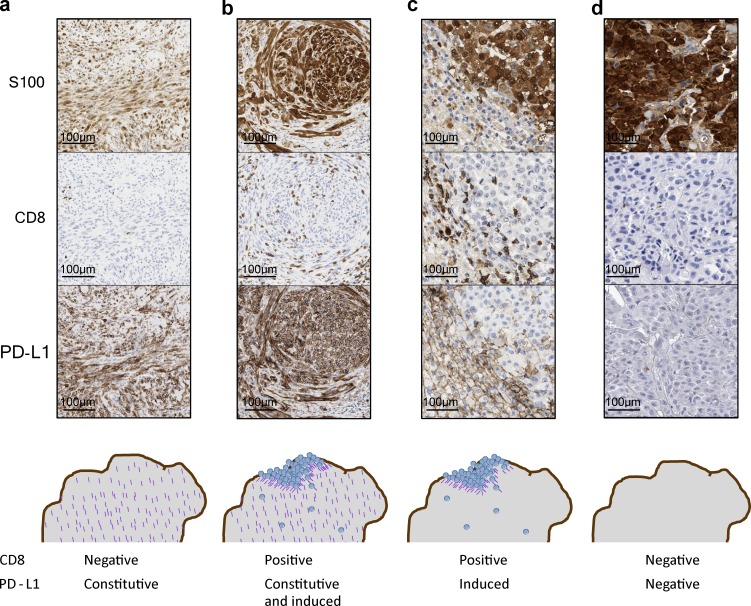
Figure 1.
Examples of different mechanisms leading to PD-L1 positivity or negativity. (a) Constitutive PD-L1 expression but no T cell infiltrate, resulting in constitutive PD-L1 expression in all cancer cells. (b) Constitutive PD-L1 expression with additional inducible expression by a T cell infiltrate, resulting in both constitutive and inducible PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. (c) Adaptive immune resistance, leading to reactive PD-L1 expression induced in cells that are at the site of a CD8+ T cell infiltrate. (d) PD-L1–negative tumor caused by absent T cell infiltration. By IHC, a tumor with JAK1/2 loss of function mutations and genetically negative for inducible PD-L1 would look similar without a CD8 T cell infiltrate (because of a lack of chemokine production in response to interferon-γ) and no PD-L1 expression in the tumor.