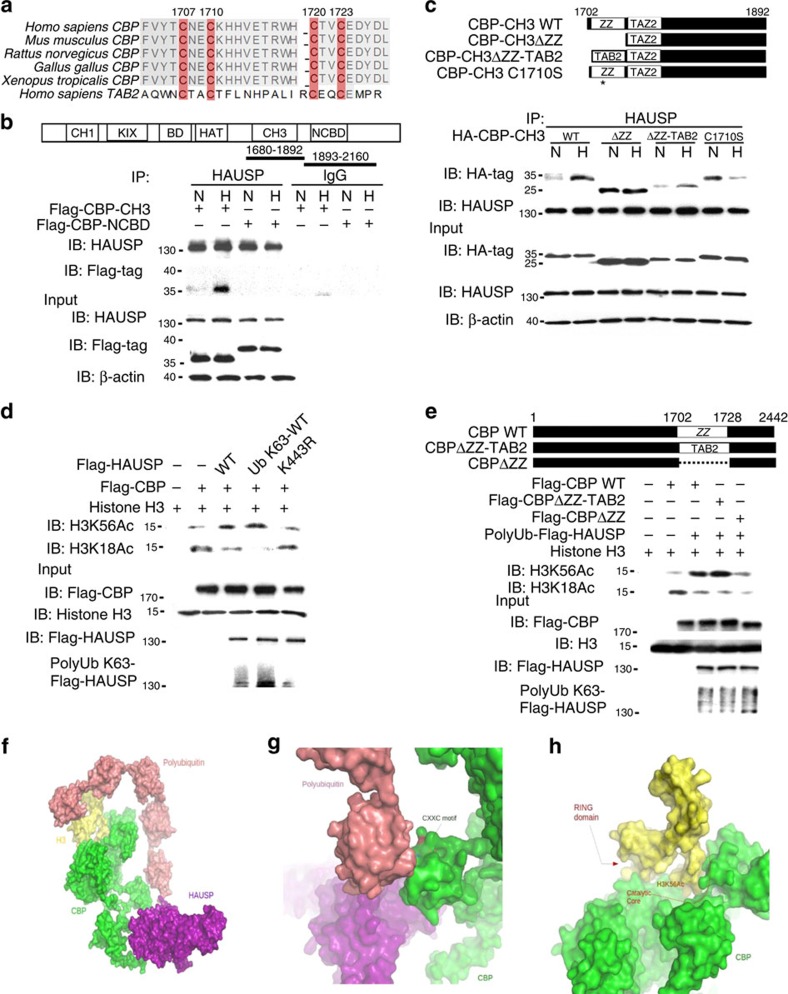
Figure 5. Interaction of HAUSP with a ubiquitin receptor (CBP) and a simulation model of the CBP-polyubiquitinated HAUSP-histone 3 complex.
(a) The homology comparison between the ZZ-type zinc finger motifs of CBP from different species and the zinc finger motifs of human TAB2. (b) Co-immunoprecipitation assays showed that the increased interaction between the CBP CH3 domain and HAUSP under hypoxia when the indicated proteins were overexpressed in 293T cells. (c) The upper panel shows the schematic diagram of CBP and different CBP mutants. The lower panel shows the increased interaction between the CBP CH3 domain/TAB2 zinc finger motifs substituted CBP and HAUSP under hypoxia by co-immunoprecipitation assays in 293T cells overexpressing these indicated proteins. There was no increased interaction between the CBP CH3 domain-ZZ-type zinc finger motif deleted/mutated and HAUSP under hypoxia. (d) In vitro histone acetylation assays showed that the H3K56 acetylation levels were maximally induced by K63-polyubiquitinated HAUSP compared to the HAUSP wild type or HAUSPK443R mutant, whereas H3K18 acetylation was drastically decreased in the presence of K63-polyubiquitinated HAUSP. (e) The upper panel shows the schematic diagram of CBP and different CBP mutants. The lower panel shows that the CBP wild type and CBP with the ZZ-type zinc finger motif substituted by Zinc-finger of TAB2 increased the H3K56Ac levels in the presence of K63-polyubiquitinated HAUSP, whereas the CBP mutant with deleted ZZ-type zinc finger motif did not increase the H3K56Ac levels. The H3K18Ac levels were used as controls. (f) A hypothetical model of three-dimensional macromolecular structures and complexes involving K63-polyubiquitined HAUSP, CBP and H3. (g) An enlarged view of the hypothetical model showed the interaction between CXXC motif of CBP and the polyubquitin chain. (h) An enlarged view of the hypothetical model showed that the region surrounding H3K56 entered into the catalytic core between the HAT and RING domains of CBP. The RING domain is located in the a.a. 1204–1278 region of CBP. Protein surface models were used to depict the models in f–h.