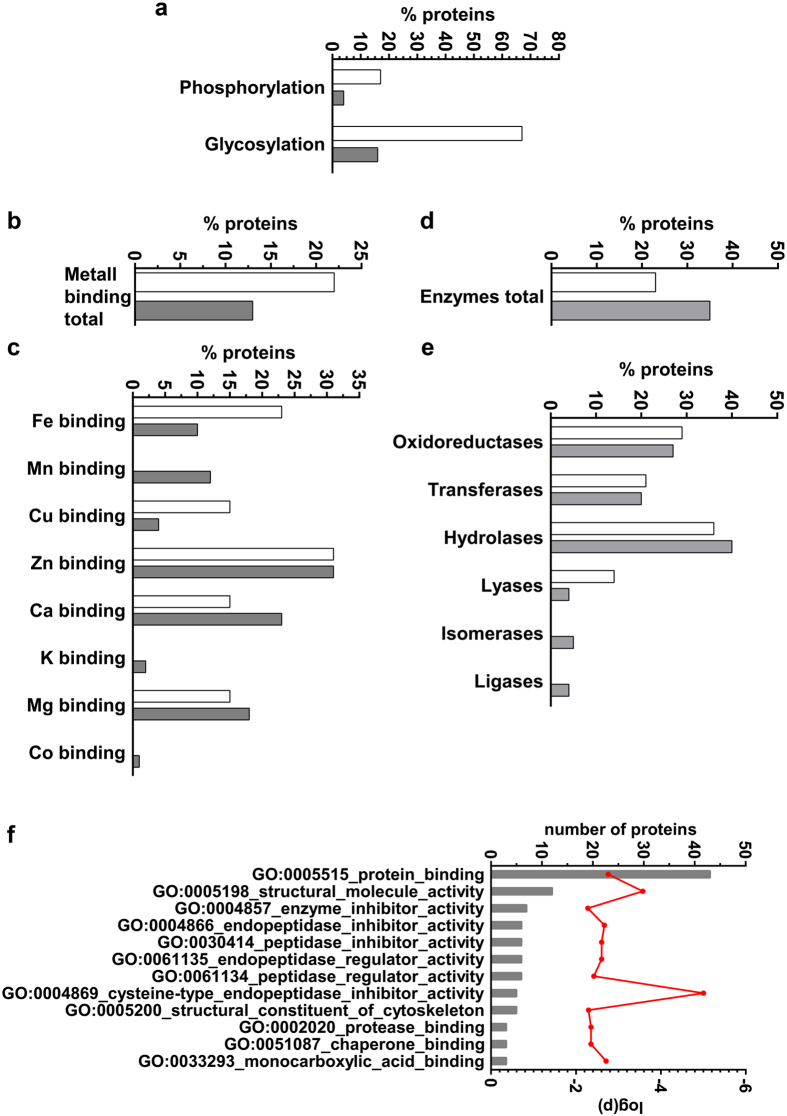
Figure 5. Post-translational modification, metal ion binding and enzymatic functions of pellicle and salivary proteins.
(a) Proteins of the pellicle (white) were more often phosphorylated and glycosylated (p < 0.0001). (b,c) Potential to bind to metals differed between both proteomes. Binding of cobalt, potassium and manganese was limited to salivary proteins (grey). (d,e) Proportion of proteins with enzymatic function. The salivary proteome (grey) included all six main enzyme classes. Pellicle (white) enzyme functions were limited to oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases and lyases. (f) Gene ontology enrichment analysis reveals functional differences between the proteome of the pellicle and the saliva. The proteins in the pellicle were enriched for enzyme regulatory functions and included a higher potential to bind to other proteins (p = 0.0016). Protein counts per category is represented by grey bars, the red line indicates calculated p-values for each ontology. Mann-Whitney-U test was archived for statistical comparison.