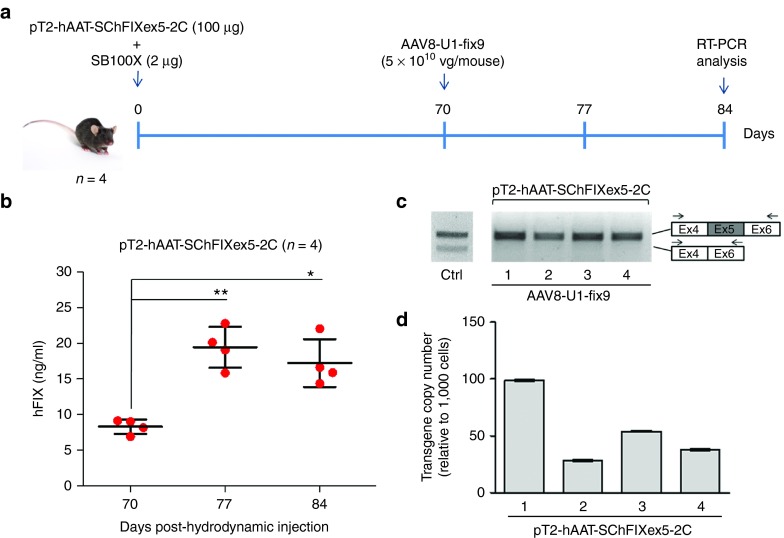
Figure 4.
Optimization of the protocol used generate the mouse model of the human FIXex5-2C splicing mutation and analyses of the rescue by systemic delivery of AAV8-U1-fix9. (a) Schematic representation of the optimized protocol used in C57BL/6 mice: 100 µg of the pT2-hAAT-SChFIXex5-2C transposon plasmid and 2 µg of the SB100X-expressing plasmid were delivered by hydrodynamic injection. Mice were followed for 70 days and then injected via tail vein with the AAV8-U1-fix9 (5 × 1010 vg/mouse). Blood samples were collected every 2 weeks posthydrodynamic injection up to 84 days. (b) Circulating hFIX levels measured by anti-hFIX ELISA on plasma samples and analyzed in triplicate. Mean values of hFIX concentration ± SD are shown at each time point. t-test, *P-value < 0.05, **P-value < 0.01. (c) RT-PCR analyses of hFIX mRNA on mouse liver samples. A positive control is represented by PCR amplification of the pT2-hAAT-SChFIX-wt plasmid (lane Ctrl). RT-PCR products were separated by electrophoresis on 2% agarose gel. The position of the primers used for the RT-PCR analyses is depicted. (d) Copy number of the transposon cassettes in C57BL/6J mouse liver DNA determined by qPCR. Values reported are mean ± SD derived from samples analyzed in triplicate. AAV, adeno-associated virus; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; qPCR, quantitative PCR; RT-PCR, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; SChFIX, splicing-competent human FIX transgene variants; SB100X, Sleeping Beauty transposon system; SD, standard deviation; U1-fix9, ExSpeU1 fix9.