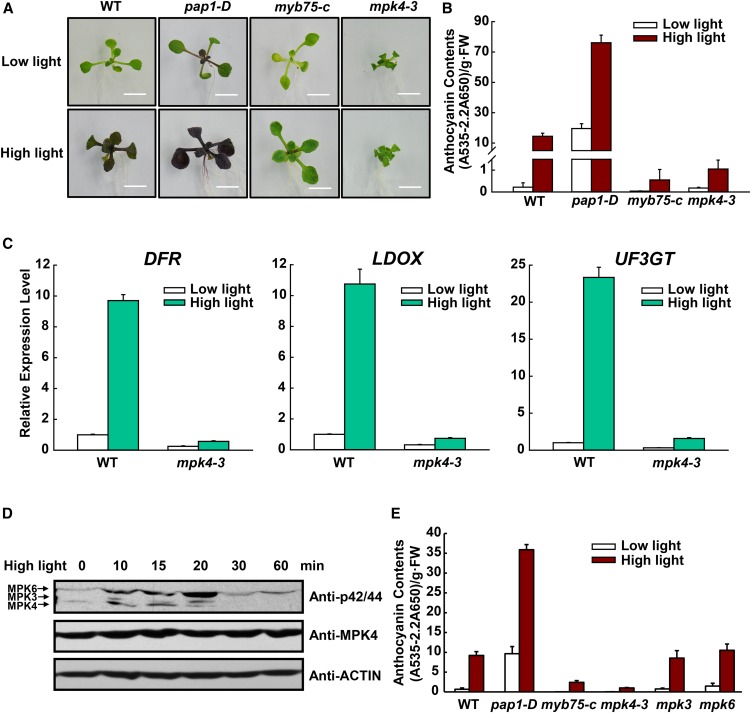
Figure 2.
MPK4 Is Involved in High Light-Induced Anthocyanin Accumulation.
(A) Twelve-day-old Arabidopsis seedlings of the wild type, pap1-D, myb75-c, and mpk4-3 grown on plates under low light or moderate high light (high light). Bars = 0.5 cm.
(B) Anthocyanin contents of the seedlings in (A). FW, fresh weight. Error bars represent sd of three replicates (representing three separate extractions from separate samples of pooled aboveground tissue of seedlings grown on one plate for each genotype and treatment).
(C) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of DFR, LDOX, and UF3GT transcript levels in 12-d-old wild-type and mpk4-3 seedlings grown on plates exposed to low light and moderate high light (high light) for 9 h, respectively. Results were normalized to ACTIN8, and expression levels of the genes in the wild type under low light were set at one unit. Error bars indicate sd of three replicates (as described above).
(D) High light-induced MAPK activation. Twelve-day-old seedlings were exposed to high light and collected at the indicated time points. MAPK activity was analyzed by immunoblot with Phospho-p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2) antibody (top panel), the level of MPK4 was determined by immunoblotting (middle panel), and ACTIN was used as a protein loading control (bottom panel).
(E) High light-induced anthocyanin accumulation is not affected in the mpk3 and mpk6 mutants. Twelve-day-old Arabidopsis seedlings were grown on plates under low light and moderate high light (high light). FW, fresh weight. Error bars represent sd of three replicates (as described above).