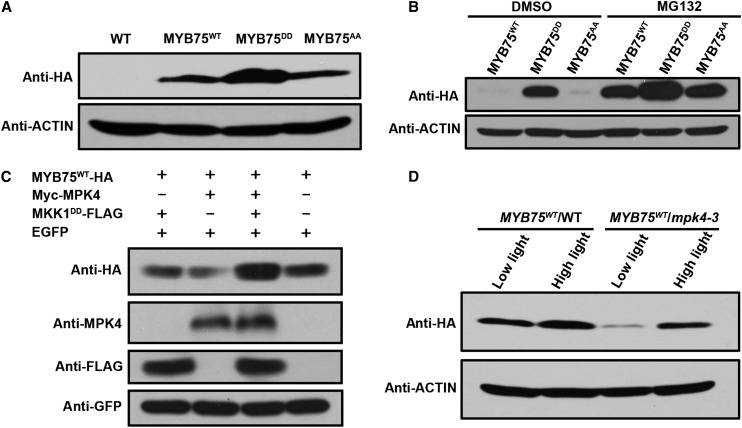
Figure 7.
Phosphorylation of MYB75 by MPK4 Increases Its Stability.
(A) Immunoblot analysis showing accumulation of the MYB75 variants in 35S:MYB75WT, 35S:MYB75DD, and 35S:MYB75AA transgenic seedlings in the wild-type background under low light. The levels of these MYB75 variants were determined by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. ACTIN was used as loading control.
(B) Phosphomimic alteration increases MYB75 stability. Dark-adapted, transgenic seedlings expressing 35S:MYB75WT, 35S:MYB75DD, and 35S:MYB75AA were treated with MG132 or DMSO for 12 h in darkness. The levels of these MYB75 variants were determined by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. ACTIN was used as loading control.
(C) Coexpression of MPK4 and MKK1DD increases the stability of MYB75. MYB75WT-HA was coexpressed with Myc-MPK4 and MKK1DD-FLAG in the leaves of N. benthamiana by agroinfiltration. EGFP was coexpressed as an internal control. “+” and “−” denote presence and absence of the protein in each sample.
(D) MPK4 regulates the stability of MYB75 in planta. 35S:MYB75WT/WT and 35S:MYB75WT/mpk4-3 were segregated from the same transformed mpk4-3 heterozygous plants. Twelve-day-old seedlings grown on plates were exposed to low light or moderate high light (high light) for 9 h. Immunoblot analysis showing the differential accumulation of MYB75WT in the wild-type and mpk4-3 backgrounds under both low light and moderate high light (high light).