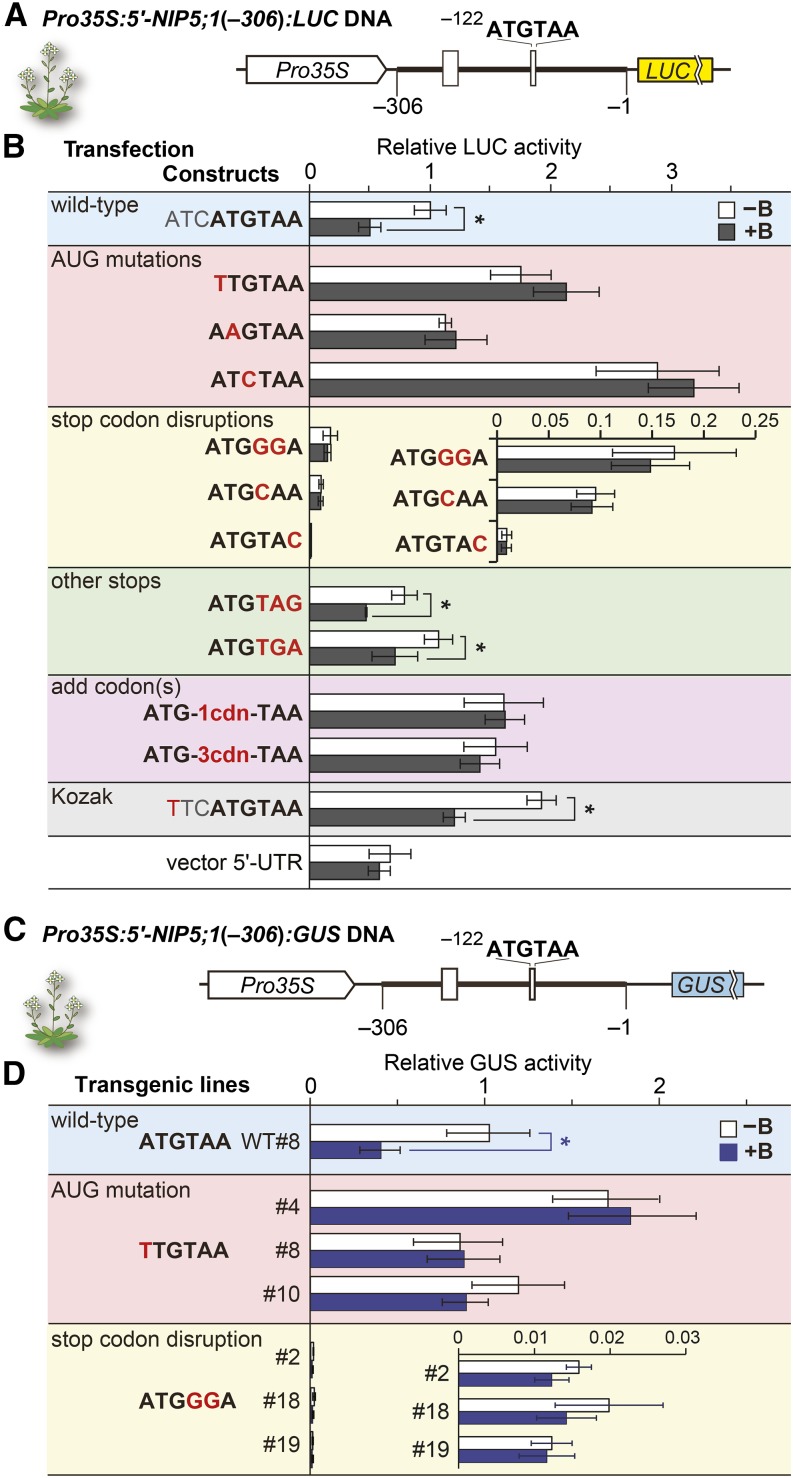
Figure 1.
B-Dependent Downregulation of NIP5;1.
(A) Schematic representation of Pro35S:5′-NIP5;1(−306):LUC DNA. Open boxes represent uORFs. The thick line represents the sequence corresponding to the 5′-UTR of NIP5;1. Nucleotide numbers are relative to the translation start site (+1). The thin lines represent 18- and 15-nucleotide linker sequences at the 5′ and 3′ ends, respectively, of the 5′-UTR.
(B) Transfection experiments using cultured Arabidopsis cells. Constructs represent the sequences of, and around, the AUGUAA in each construct with the altered nucleotides shown in red. Transfected protoplasts were incubated under 500 μM B (+B) or 1 μM B (−B) conditions. The LUC activity of each transfected cell extract was normalized with RLUC activity from the cotransfected internal control plasmid and shown as the relative LUC activity. Means ± sd of relative LUC activities are shown (n = 3). Asterisks indicate a significant reduction in +B compared with −B conditions (P < 0.05). The “vector 5′-UTR” negative control carries only the vector’s 5′-UTR sequence. The nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequences of ATG-1cdn-TAA and ATG-3cdn-TAA are shown in Supplemental Figure 2C.
(C) Schematic representation of Pro35S:5′-NIP5;1(−306):GUS DNA. The thin lines represent 37- and 59-nucleotide linker sequences at the 5′ and 3′ ends, respectively, of the 5′-UTR.
(D) Effect of B on GUS activities in transgenic plants. Transgenic plants were grown under 100 µM B (+B) or 0.3 µM B (−B) conditions. Relative GUS activities in roots were determined. Transgenic line WT#8 carries a wild-type −122AUG-stop (Tanaka et al., 2011). Three each of independent transgenic lines were used for the mutant constructs. Means ± sd of GUS activities relative to that of WT#8 under −B are shown (n = 4 to 5). Asterisks indicate significant reductions under +B conditions (P < 0.05).