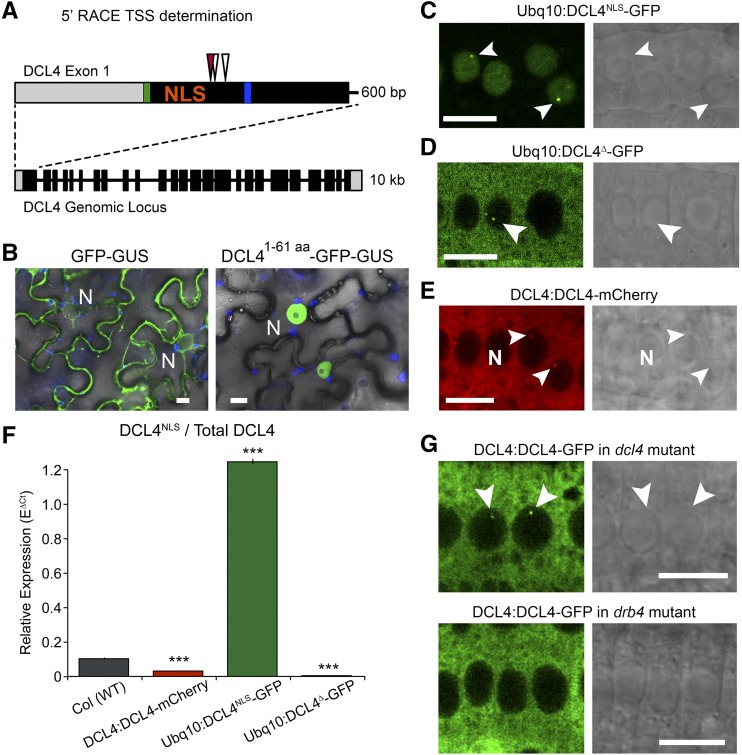
Figure 2.
DCL4∆ Isoform Predominates and Encodes a Cytoplasmic Protein.
(A) Illustration of DCL4 locus and detailed view of exon 1. Exons, blocks; introns, lines; UTR, gray; ATGs highlighted in green and blue. TSS determined by direct sequencing of bulk PCR products from nested RACE PCR are depicted with arrowheads: Col wild type (white) and ProDCL4:DCL4-mCherry (red).
(B) Images of GFP-GUS (left) or GFP-GUS fused to the first 61 amino acids of DCL4 (right) expressed from UBQ10 promoter in N. benthamiana leaves. Overlaid with chlorophyll autofluorescence (blue) and bright field (differential interference contrast).
(C) Confocal images of fluorescent signal and bright field (differential interference contrast; right) from roots of Arabidopsis plants transformed with Ubq10 promoter-driven GFP fusions to the genomic coding sequence of DCL4NLS,
(D) Genomic coding sequence of DCL4∆, corresponding to the TSS determined by RACE sequencing.
(E) DCL4 native promoter fused to the full DCL4 genomic coding sequence, including NLS, fused to mCherry.
(F) Relative expression by qRT-PCR of DCL4NLS normalized to total DCL4 in Col and transgenic seedlings. Mean ± se of three independently harvested biological replicates, each with three technical replicates shown. ***P value < 0.001 in t test relative to Col.
(G) Confocal images of ProDCL4:DCL4-GFP in roots of dcl4 (top) or drb4 mutant plants (bottom).
Images represent consistent results in at least three independent transgenic lines. Dicing bodies indicated with arrowheads. Bars = 10 μm.