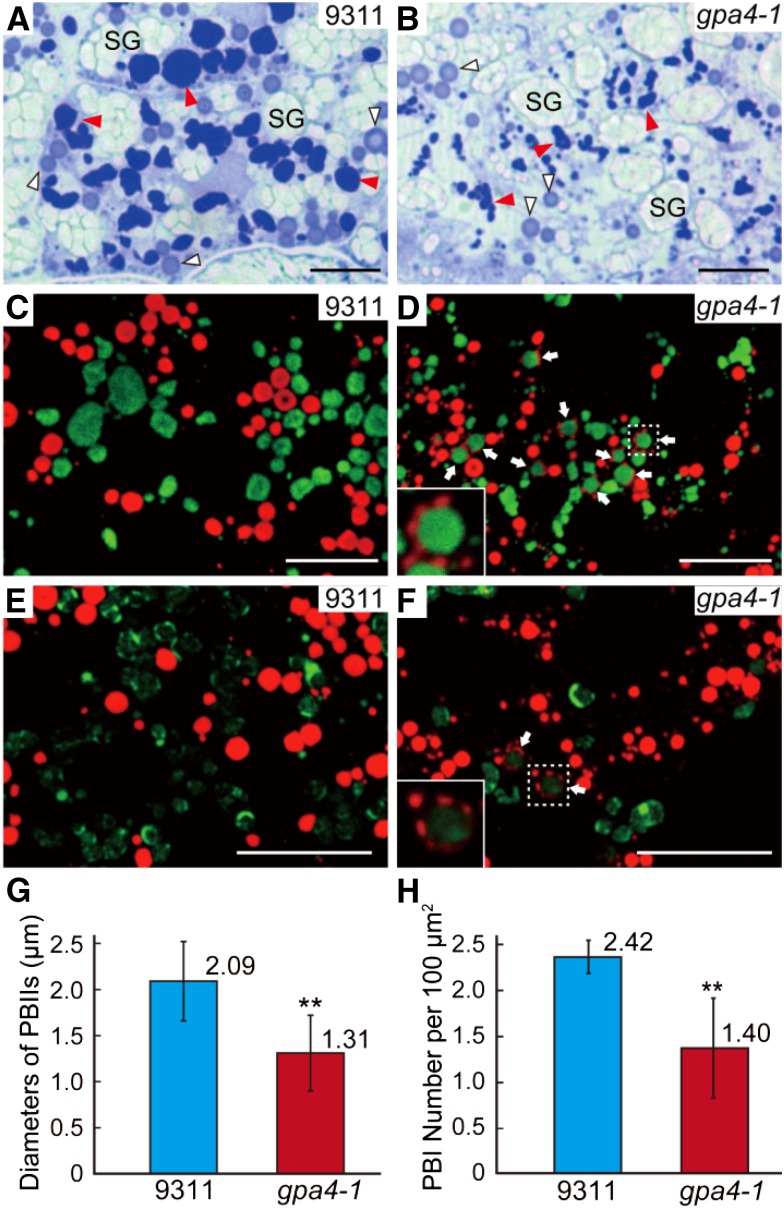
Figure 2.
Light and Immunofluorescence Microscopy of Protein Bodies in the Subaleurone Cells of the Wild Type and the gpa4-1 Mutant.
(A) and (B) Sections of 12 DAF endosperm of the wild type (A) and gpa4-1 (B) stained with Coomassie blue. Red and white triangles indicate the dark-stained glutelin-containing structures (PBIIs in the wild type) and the light-stained prolamin-containing structures (PBIs in the wild type), respectively. SG, starch grains. Bars = 10 μm.
(C) to (F) Immunofluorescence microscopy images of storage proteins in wild-type ([C] and [E]) and gpa4-1 ([D] and [F]) seeds. Secondary antibodies conjugated with Alexa fluor 488 (green) and Alexa fluor 555 (red) were used to trace the antigens recognized by the antiglutelin and antiprolamin antibodies, respectively, in (C) and (D). Similar reactions were performed with anti-α-globulin antibodies instead of antiglutelin antibodies in (E) and (F). White arrows in (D) and (F) indicate the novel structures. The insets in (D) and (F) are the enlarged images of the corresponding boxed areas. Bars = 10 μm.
(G) and (H) Measurement of the diameters of PBIIs (G) and the number of PBIs with normal size per 100 µm2 (H). Values are mean ± sd. **P < 0.01 (n = 84 for the wild type and 56 for gpa4-1 in [G]; n = 4 [total 470 PBIs] for the wild type and 5 [total 334 PBIs] for gpa4-1 in [H]; Student’s t test).