Fig. 2.
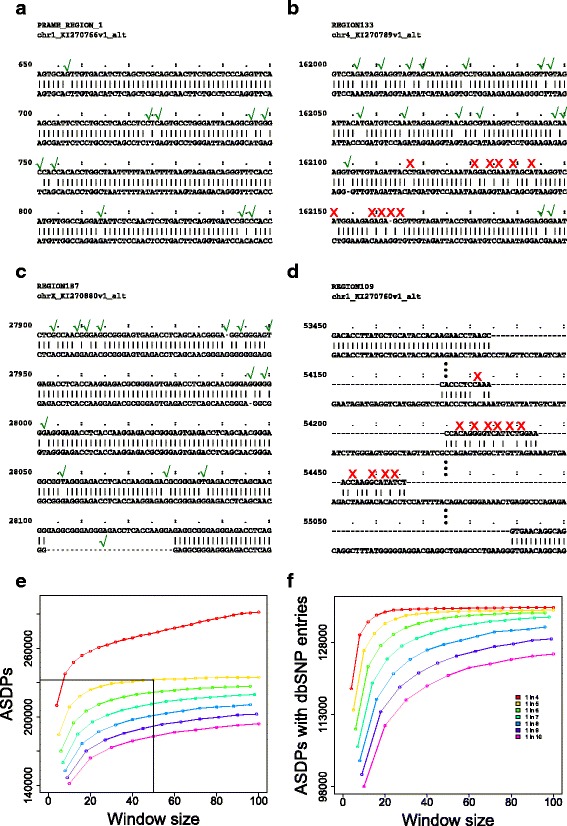
Frequency of ASDPs. Alignments contain stretches of sequences that are largely but not entirely identical between the primary assembly and an alternate locus, ranging from regions that are nearly identical to those with a substantial number of differences. ASDPs were defined to be positions of the alignment that differ between REF-HAP and ALT-HAP and are located in a sliding window in which at most 10 of 50 nucleotides are discrepant (green check marks). The red crosses show discrepancies that are excluded by this definition. In a and c, no ASDP was filtered out by the sliding window whereas in b, stretches of low sequence identity lead to the removal of several positions shown as red crosses. In d, large inserts in the ALT-HAP lead to a larger number of discrepant positions, which are discarded by the above criteria. e The effects of applying different thresholds of allowed discrepancies and window sizes to call ASDPs. The dotted lines mark the mismatch frequency (ten mismatches in 50 bases) used in this work. f Number of ASDPs that overlap with dbSNP variants according to the different thresholds. ASDP alignable scaffold-discrepant position
