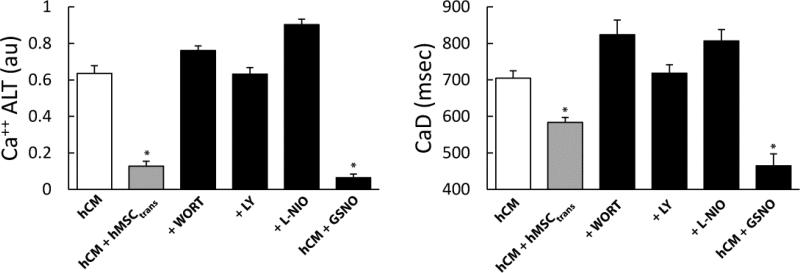
Figure 7.
The effects of PI3K inhibitors (Wortmannin, LY294002), eNOS inhibitor and no donor GSNO under conditions of oxidative stress. Graphs show summary data of Ca++ ALT (left) and CaD (right) for hCM alone, hCM+hMSCtrans, hCM+hMSCtrans+Wortmannin (+WORT), hCM+hMSCtrans+LY294002 (+LY), hCM+hMSCtrans+eNOS inhibitor (+L-NIO) and hCM+GSNO. PI3K and eNOS inhibitors significantly increased Ca++ ALT (n=8, p< 0.0001) and CaD (n=8, p< 0.0001). In contrast, Ca++ ALT (n=6, p< 0.0001) and CaD (n=6, p< 0.0001) were significantly decreased by GSNO in absence of hMSC. This suggests a mechanism of action related to PI3K mediated nitroso-redox pathway.