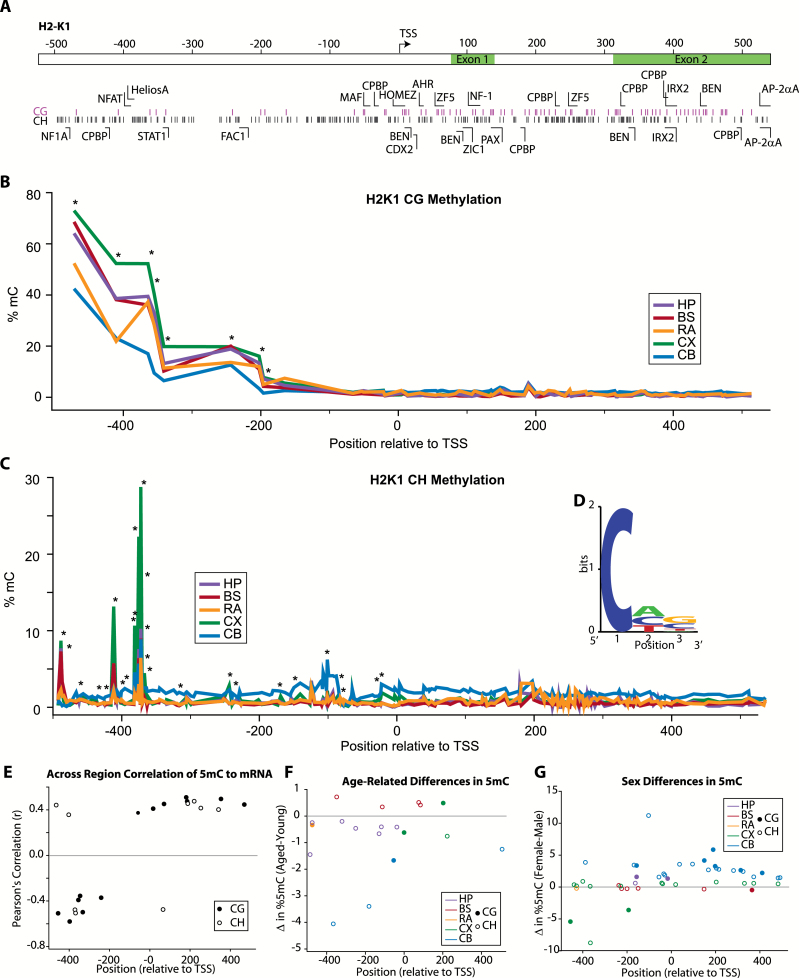
Figure 5.
CG and non-CG methylation of H2-K1 promoter and intragenic regions. (A) Schematic of region analyzed, locations of CG and non-CG sites, and transcription factor binding domains. (B) Topography of site-specific CG methylation level in H2-K1 for each of the CNS regions analyzed. Average methylation at each site is presented. Sites with differential methylation between regions (one-way ANOVA, *p < .05) are noted. (C) Low levels of non-CG methylation were detected with the exception of specific peaks of higher (>5%) methylation. Average methylation at each site is presented. Sites with differential methylation between regions (one-way ANOVA, *p < .05) are noted. (D) Non-CG methylation has been proposed to be enriched in specific motifs, and the enrichment of specific nucleotides was examined for the non-CG sites with the highest (>average for the region examined) methylation levels. (E) H2-K1 expression across CNS regions was correlated to paired methylation levels from the same animals at specific CG and non-CG sites. Only young animals were analyzed to control for age-related differences in gene expression. Among sites with significant correlations (Pearson correlation α > 0.05 r > |0.25|), methylation at CG and CH sites in the promoter region was overall negatively correlated with gene expression, whereas methylation at intragenic CG and CH sites was positively correlated. (F) Age- and (G) sex-related differences in CG and non-CG methylation levels were evident across the H2-K1 region examined. Overall, observed age-specific differences were primarily decreases in methylation with increased age. The majority of differences in methylation observed between sexes were increases in methylation in females vs. males. Only sites with statistically significant differences are shown [two-way ANOVA (Age × Sex), Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc p < .05 within each CNS region], sites are color coded by brain region examined (HP-hippocampus, BS-brainstem, RA-retina, CX-cortex, CB-cerebellum) and whether the site is a CG (filled circle) or non-CG/CH (open circle) is noted. n = 3–4/group (age/sex/region).