FIG 2 .
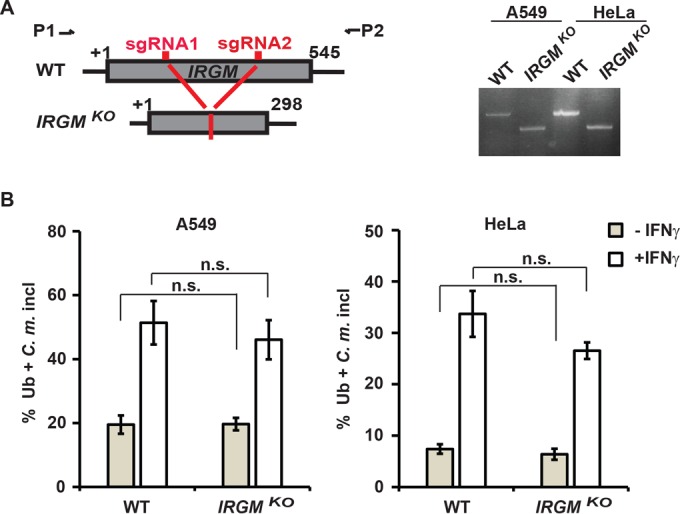
Human IRGM is dispensable for the ubiquitination of C. muridarum inclusions. (A) CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing was used to generate deletions of approximately 230 bp in the coding sequence of human IRGM. The locus was targeted using two small guide RNAs (sgRNA1 and sgRNA2), and individual cell clones were isolated from parental A549 and HeLa cell lines and confirmed for deletions in the IRGM gene by PCR. (B) Parental (wild type [WT]) and IRGMKO (KO stands for knockout) A549 and HeLa cells were infected with C. muridarum (C. m.) and primed with IFN-γ (100 U/ml) at 3 hpi or left unprimed. At 20 hpi, the cells were stained for ubiquitin (FK2) and C. muridarum (anti-Slc1). Colocalization of ubiquitin with inclusions in A549 cells and HeLa cells was quantified as described in Materials and Methods. At least 100 inclusions were counted for each condition. Values that are not statistically significantly different (n.s.) by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test are indicated. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Values are means ± standard deviations (SD) (error bars).
