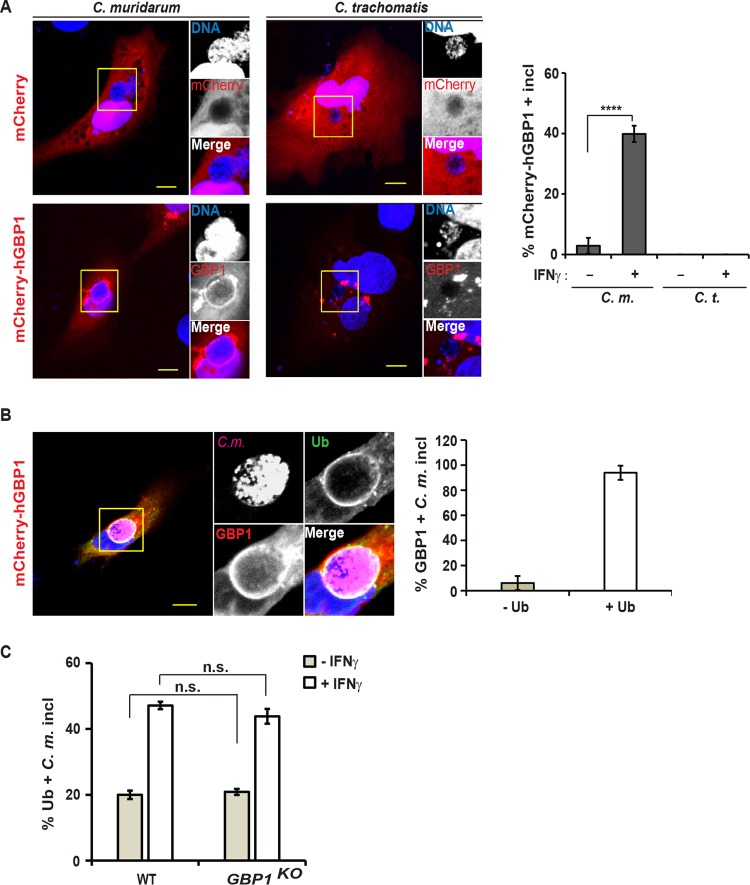
FIG 5 .
Human GBP1 targets ubiquitin-positive inclusions. (A) A549 cells were transfected with an mCherry-hGBP1 expression construct and 24 h later infected with C. muridarum or C. trachomatis at an MOI of 2 and primed with IFN-γ (100 U/ml) at 3 hpi or left unprimed. At 20 hpi, the cells were fixed and stained with Hoechst. (Left) Representative images are shown. Bars = 10 μm. (Right) Percentage of mCherry-GBP1-positive inclusions in mCherry-expressing cells was quantified. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Values are means ± SD (error bars) (n = 3). Values that are significantly different (P < 0.001) by Student’s t test are indicated by a bar and four asterisks. (B) Experiment was performed as described above for panel A, except for staining cells additionally with anti-ubiquitin (FK2) and anti-Chlamydia (Slc1) antibodies. (Left) Representative images are shown. (Right) Ubiquitin staining of hGBP1-positive inclusions was quantified. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Values are means ± SD (n = 3). (C) Parental (WT) and GBP1KO A549 cells were infected with C. muridarum and primed with IFN-γ (100 U/ml) at 3 hpi or left unprimed. At 20 hpi, colocalization of ubiquitin (FK2) with inclusions was quantified. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Values are means ± SD. Values that are not significantly different (n.s.) are indicated.