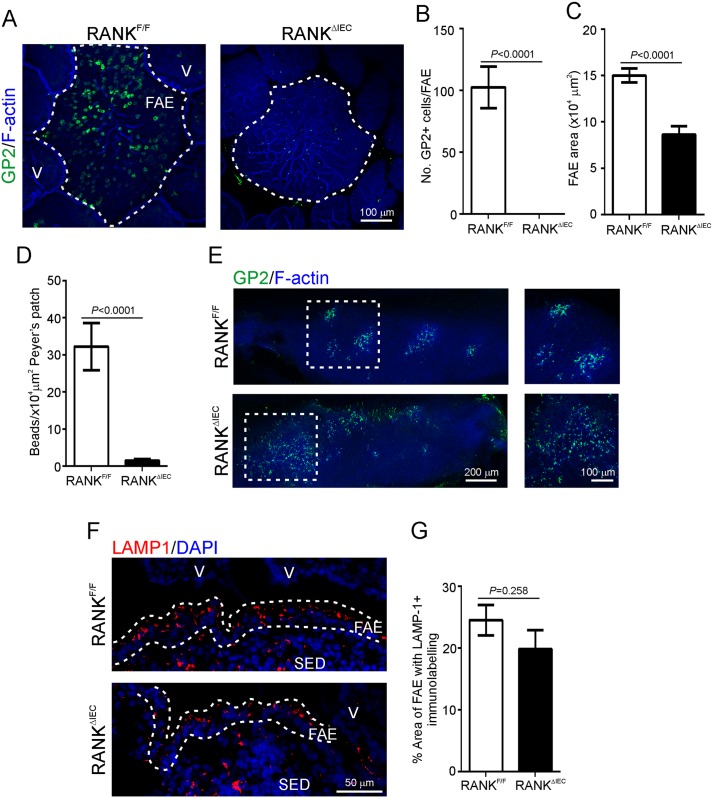
Fig 1. RANKΔIEC mice specifically lack intestinal M cells.
A) Peyer’s patches from RANKF/F and RANKΔIEC mice were whole-mount immunostained to detect M cells (GP2+ cells, green) and F-actin (blue) as a counterstain. The broken line indicates the boundary of the follicle associated epithelium (FAE) overlying the Peyer’s patches. V, villi. This immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis indicated an absence of GP2+ M cells in the FAE of RANKΔIEC mice. B) Morphometric analysis confirmed that the number of GP2+ cells/FAE was significantly reduced in RANKΔIEC mice (P<0.0001, Mann-Whitney U test). C) The size of the FAE area was also significantly reduced in RANKΔIEC mice (P<0.0001, Student’s t-test; data derived from 4 FAE/mouse, n = 3–5 mice/group). D) To compare the functional ability of M cells in the FAE of RANKΔIEC and RANKF/F control mice to transcytose particulate antigens, mice were orally gavaged with 200 nm fluorescent microbeads and 24 h later, the presence of the microbeads in their Peyer’s patches was determined by fluorescence microscopy. The uptake of microbeads into the Peyer’s patches of RANKΔIEC mice was significantly impaired when compared to RANKF/F mice (P<0.0001, Mann-Whitney U test; data derived from 21–31 sections of Peyer’s patches/mouse, n = 3 mice/group). E) Whole-mount IHC analysis revealed that GP2+ M cells (green) were abundant in the nasal associated lymphoid tissues of RANKF/F and RANKΔIEC mice. F-actin (blue) was used as a counterstain. The boxed area in the left-hand images is shown at higher magnification in the right-hand images. F) IHC analysis was used to compare the presence of large LAMP1+ endosomes (red) within enterocytes in FAE of Peyer’s patches from RANKF/F and RANKΔIEC mice. Sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue) to detect cell nuclei. The broken lines indicate the boundary of the FAE. SED, subepithelial dome. G) Morphometric analysis revealed that the area of the LAMP1+ immunostaining in the FAE of RANKF/F and RANKΔIEC mice was similar (P = 0.258, Student’s t-test; data derived from 2–8 FAE/mouse, n = 3 mice/group), suggesting that the formation of the large LAMP1+ endosomes in FAE enterocytes was not influenced by RANK-deficiency in the gut epithelium.