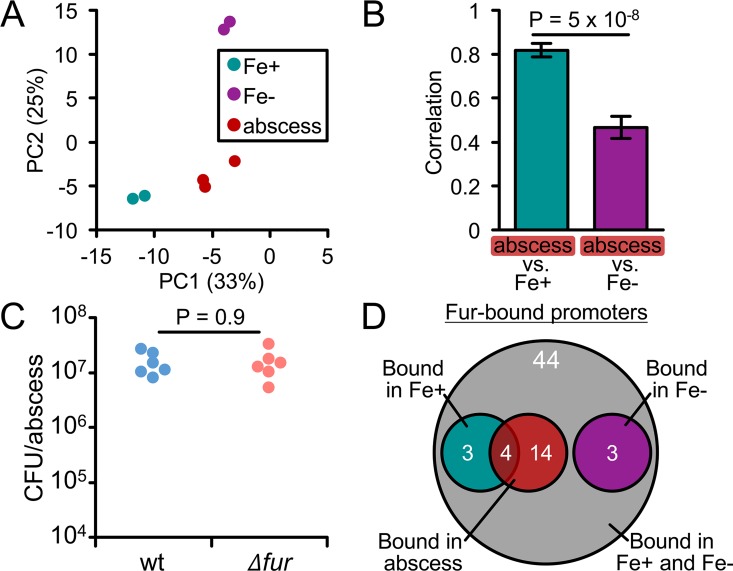
Fig 5. A. actinomycetemcomitans is not iron-restricted in murine abscess mono-infection.
(A) Principal component analysis of the 93 genes regulated by iron. Each dot is a single replicate. Legend: Fe+, biofilm on rich media; Fe-, biofilm on iron-chelated media; abscess, wild-type abscess infection. Axes: Percentages are the amount of variation captured by each principal component. (B) Correlation analysis of the 93 genes regulated by iron. Spearman’s rank correlation was determined by comparing gene expression in wild-type A. actinomycetemcomitans abscess infection to Fe+ and Fe- in vitro biofilms. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 6 pairwise comparisons). Significance was determined using a 2-tailed t test. (C) Survival of the wild type (wt) and Δfur mutant in abscesses. Each dot is a single abscess (n = 2 biological replicates). Significance was determined using a Mann-Whitney U test. Y axis represents colony forming units (CFU) per abscess after 3 days post-infection. (D) Venn diagram showing the overlap between the in vitro and in vivo ChIP-seq results.