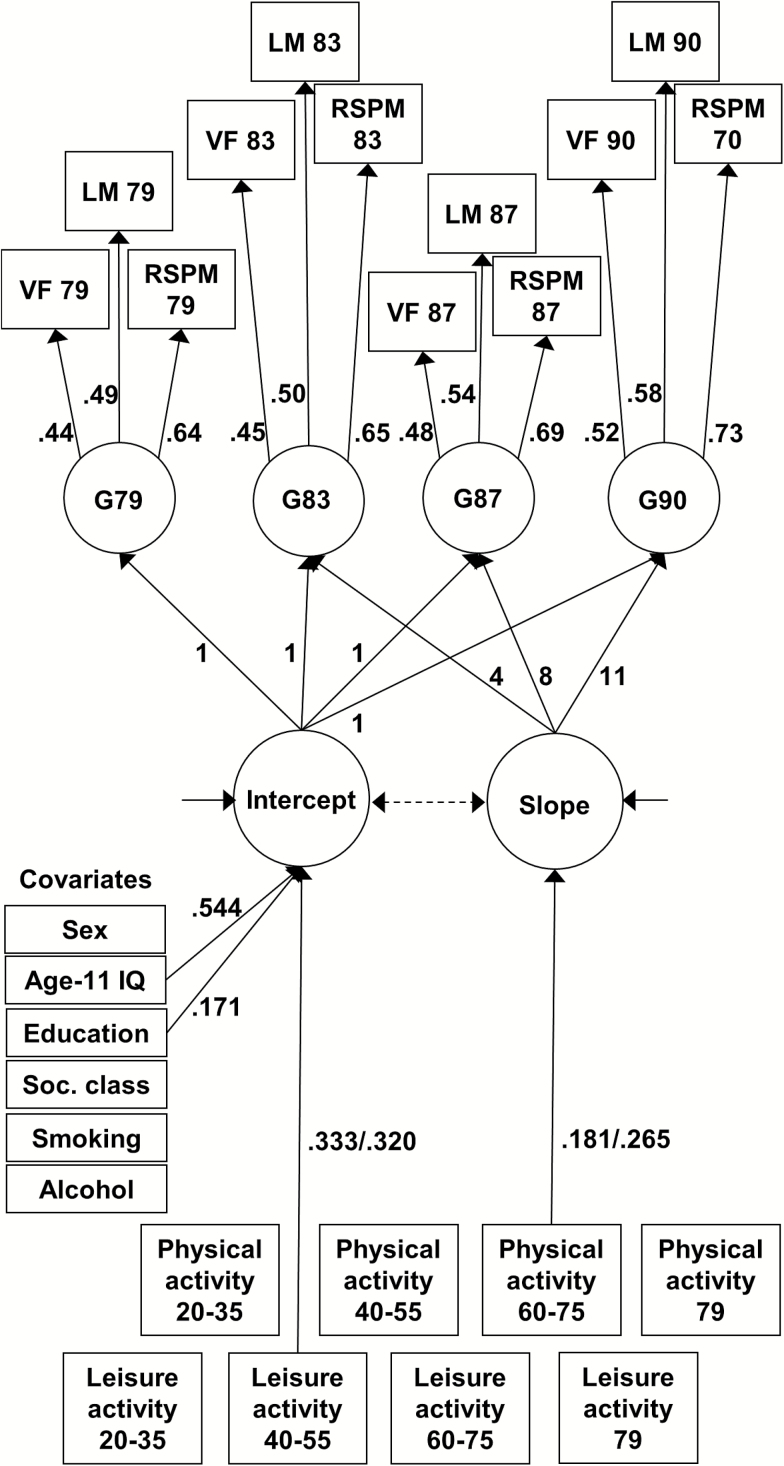
Figure 1.
Latent growth curve model of the level of, and change in, general cognitive ability over four waves of the Lothian Birth Cohort 1921. In the latent growth curve model, manifest (measured) variables are represented by rectangles and latent traits by circles. Latent general cognitive ability factors (G) were produced at each occasion from the three cognitive tests completed (VF = Verbal Fluency, LM = Logical Memory, and RSPM = Raven’s Standard Progressive Matrices). Correlations between the activity factors are given in Supplementary Table 2 and between the cognitive ability variables in Supplementary Table 4. The principal outcome variables in the model are intercept (the level of general cognitive ability) and slope (the change in general cognitive ability across time). In a growth curve model with more than two occasions, the intercept is a composite representing overall level; here, the intercept term therefore represents the composite level of cognitive ability across ages 79 (Wave 1) to 90 (Wave 4). The measured variables have fixed contributions to the intercept; the fixed contributions to slope (4, 8, and 11) represent the number of years since the initial testing occasion, age 79 in this model. Figures with decimal points are the standardized estimates generated by the model, given before/after inclusion of the covariates. Only significant paths are shown (full results in Table 2), except the path from physical activity 60–75 to slope which was not significant before inclusion of the covariates.