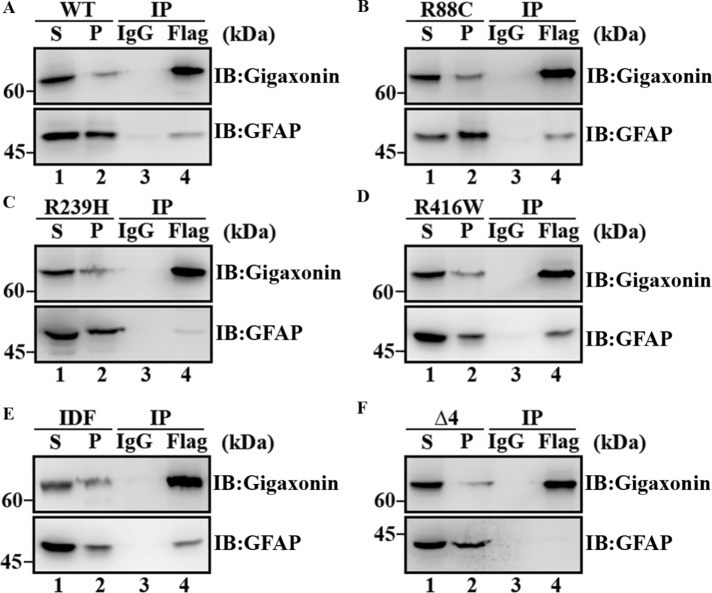
FIGURE 9:
Mutations in GFAP reduced its interaction with gigaxonin. SW13 cells stably expressing either wild-type (A) or mutant (B–F) GFAPs were infected with Flag-gigaxonin lentiviruses. At 36 h after infection, cells were extracted with a RIPA lysis buffer, and the supernatant (A–F, lane 1) and pellet (A–F, lane 2) fraction were prepared as described in Materials and Methods. The supernatant fractions were subjected to immunoprecipitation by using a mouse monoclonal anti-Flag antibody (A–F lane 4). Mouse IgG was used as a control (A–F, lane 3). The supernatant (A–F, lane 1) and pellet (A–F, lane 2) fractions, as well as the Flag (A–F, lane 4) and IgG (A–F, lane 3) immunoprecipitates, were analyzed by immunoblotting using rabbit polyclonal anti-gigaxonin (A–F, top) and anti-GFAP (A–F, bottom) antibodies. Molecular mass markers are shown on the left. R239H (C, lane 4) and ∆4 (F, lane 4) mutants that coprecipitate with gigaxonin were both decreased compared with wild-type (A, lane 4), R88C (B, lane 4), R416W (D, lane 4), and IDF (E, lane 4) GFAP. Full-length images of blots are shown in Supplemental Figure S2.