FIGURE 2:
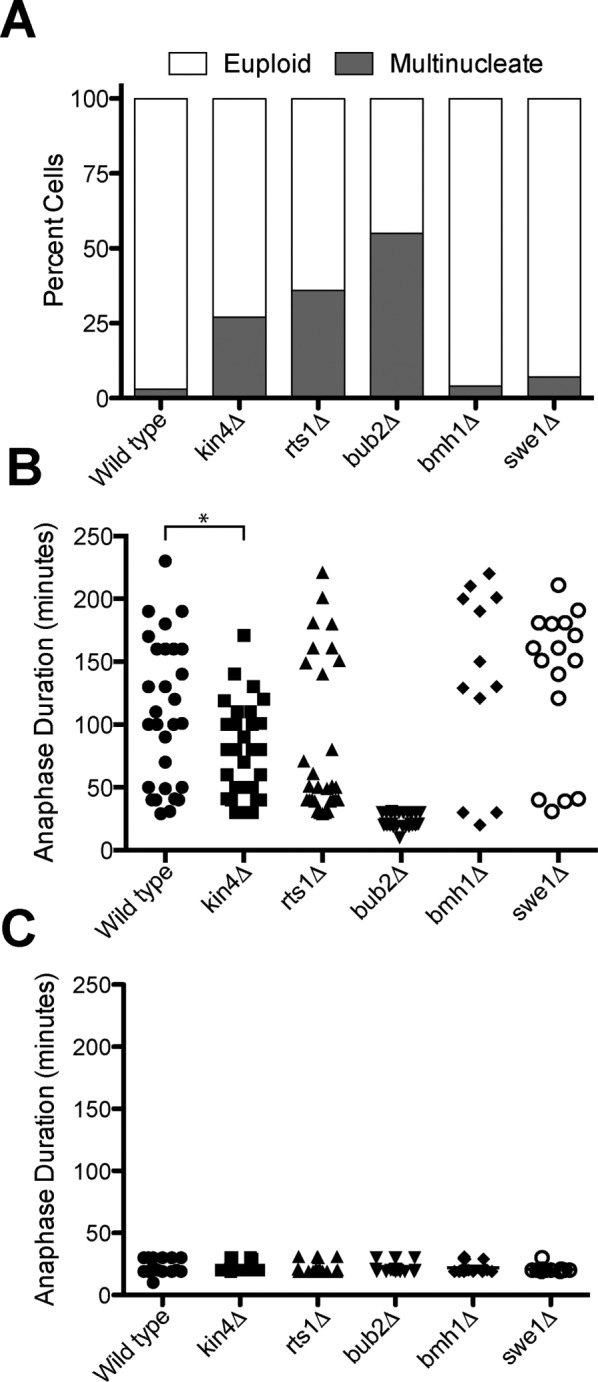
SPoC mutants retain some checkpoint activity. dyn1-AID kar9Δ (A35707), dyn1-AID kar9Δ kin4Δ (A35603), dyn1-AID kar9Δ rts1Δ (A37483), dyn1-AID kar9Δ bmh1Δ (A36544), dyn1-AID kar9Δ swe1Δ (A35146), and dyn1-AID kar9Δ bub2Δ (A36082) cells carrying GFP-tagged α-tubulin were grown in YEPD medium and arrested in the G1 phase of the cell cycle with 10 μg/ml α-factor pheromone. Cells were released into the cell cycle in YEPD medium and then monitored by live-cell microscopy in a Y04C flow cell. Depletion of dyn1-AID was induced in the flow cell with 100 μM auxin in synthetic complete medium. (A) Fraction of cells that become multinucleate. Number of nuclei was determined upon completion of the first cell cycle after factor release (n = 100). Cells that inappropriately exited from mitosis in the mother cell compartment and hence harbored two nuclei were scored as “multinucleate.” Cells that either arrested permanently with mispositioned spindles in the mother cell compartment or exited mitosis with aligned spindles were scores as “euploid.” (B, C) Anaphase duration was determined in cells that exit from mitosis with mispositioned (B) or correctly positioned (C) spindles. Sample sizes for B: dyn1-AID kar9Δ, 29; dyn1-AID kar9Δ kin4, 31; dyn1-AID kar9Δ rts1Δ, 30; dyn1-AID kar9Δ bmh1Δ, 12; dyn1-AID kar9Δ swe1Δ, 16; and dyn1-AID kar9Δ bub2Δ, 30. The p value in B is <0.05 (two-sided t test). Sample sizes for C: dyn1-AID kar9Δ, 18; dyn1-AID kar9Δ kin4, 20; dyn1-AID kar9Δ rts1Δ, 17; dyn1-AID kar9Δ bmh1Δ, 20; dyn1-AID kar9Δ swe1Δ, 20; and dyn1-AID kar9Δ bub2Δ, 19.
