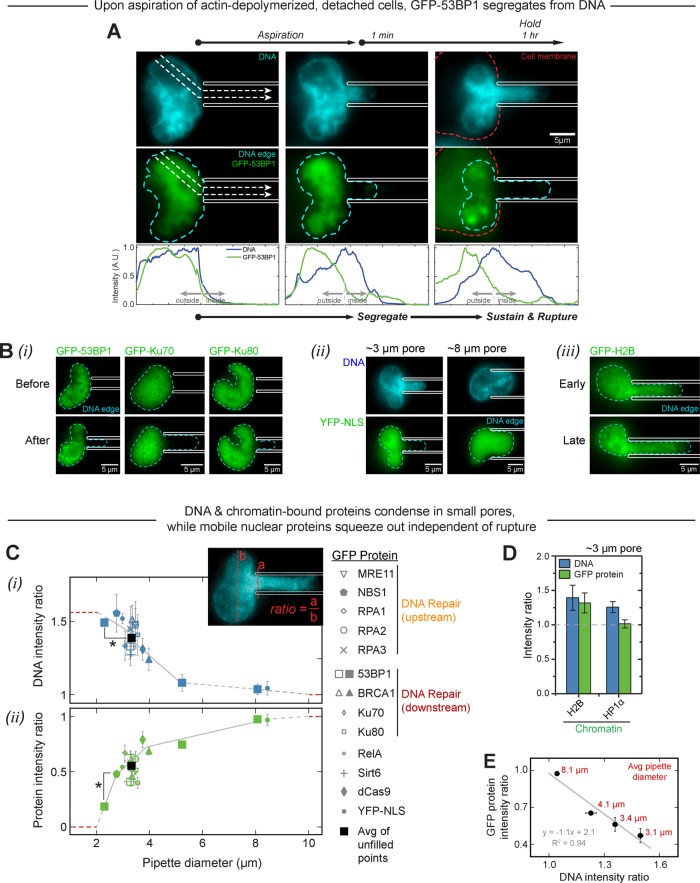
FIGURE 2:
Pulling nuclei into small micropipettes consistently compacts the chromatin and causes complementary protein segregation. (A) Cells used for aspiration are deadhered and treated with latrunculin A to depolymerize the cytoskeleton. When a cell and nucleus are then aspirated into a 3-μm pipette, chromatin intensity increases at the pipette entrance and mobile GFP-53BP1 decreases, sometimes leaking or rupturing out of the nucleus. Intensity profiles are shown along the dashed arrows (representative of at least three experiments). (B) Segregation of other mobile GFP proteins contrasts with a DNA-like profile for histone-H2B. (C) All other mobile proteins studied—including repair, transcription, and epigenetic factors, as well as a nuclease—also segregate upon aspiration into ∼3-μm pipettes (≥3 cells/group). Segregation is sensitive to pipette size: protein intensity ratio decays with decreasing diameter, vanishing at an extrapolated critical diameter of ∼2 μm. Below this critical value, the DNA intensity ratio plateaus as DNA reaches maximum compaction inside the pipette. Unfilled data points fall between 3.0 and 3.7 μm in diameter; their average is indicated by a filled black square. Solid gray lines are fits between filled points with statistically different intensity ratios, and dashed gray lines are extrapolations or fits between points that are not statistically different. YFP-NLS-MS2 was added after the fits but confirms expectations. Red dashed lines show the intensity ratio limits for small and large pipette diameter. (D) Chromatin-bound proteins do not segregate from DNA in ∼3-μm pipettes (≥4 cells/group). (E) A negative linear correlation between protein intensity ratio and DNA intensity ratio is consistent with chromatin occupying a solid volume fraction f of the nucleus while mobile proteins occupy the free volume 1 – f (see Image analysis in Materials and Methods). Data from C were binned according to average pipette diameter.