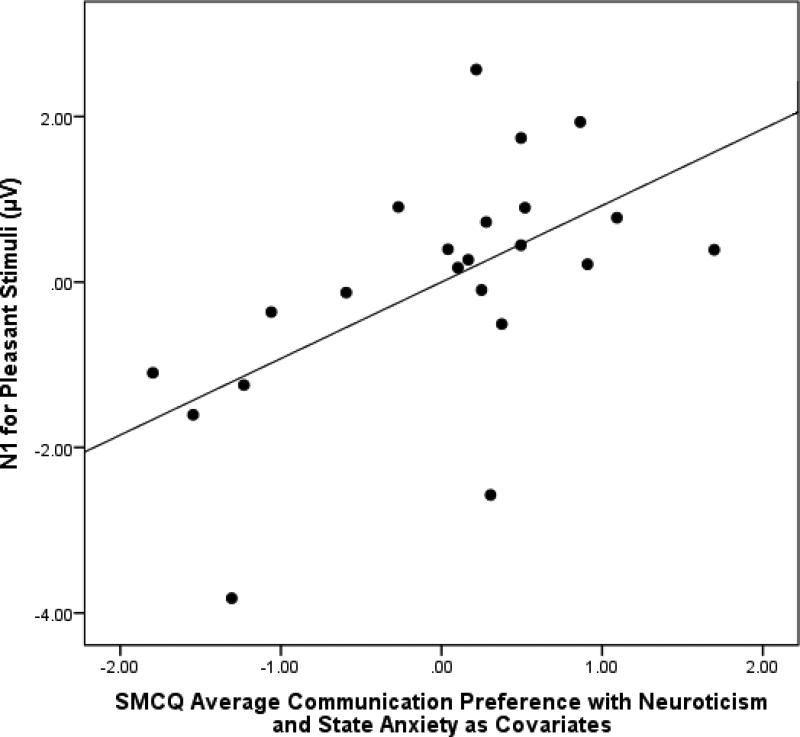
Figure 3.
A greater overall preference for CMC was associated with greater (more negative) amplitude N1 to pleasant versus neutral stimuli.
Note. The x-axis represents the sample distribution of SMCQ scores taking neuroticism and anxiety into account, ranging from − 2.00 SD (CMC preference) to +2.00 SD (face-to-face preference).