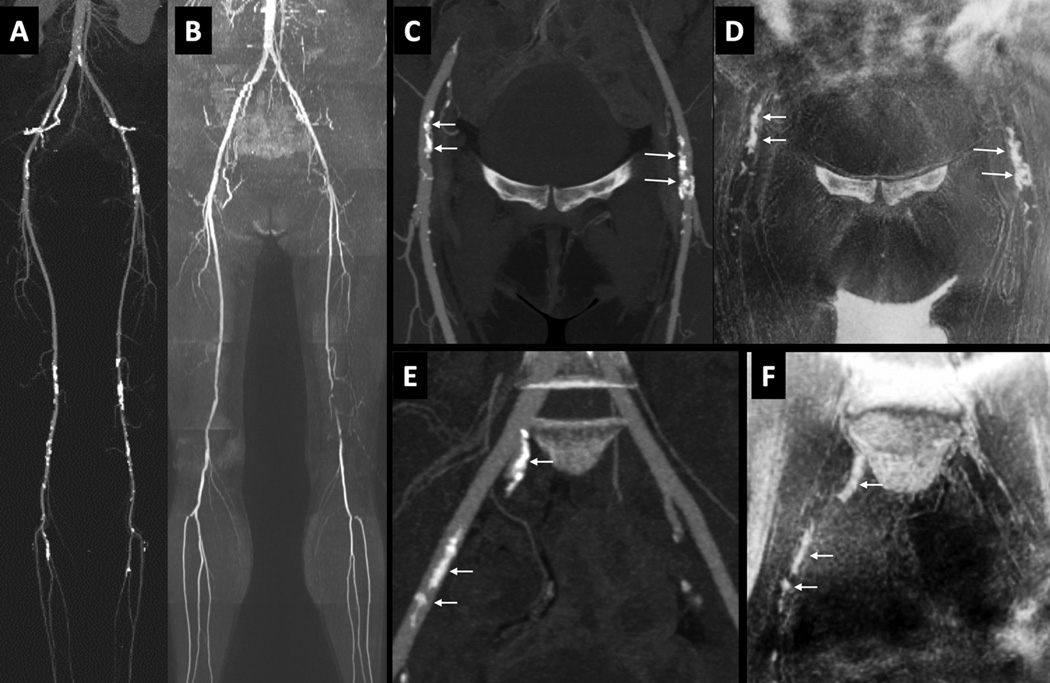
Figure 3.
51-year old female with disabling claudication involving the left lower extremity. (A) CTA. (B) QISS MRA, showing multi-focal atherosclerotic disease including a segmental occlusion of the distal left superficial femoral artery. (C) Maximum intensity projection from CTA focused to the ilio-femoral vessels. (D) Corresponding minimum intensity projection (b/w inverted) from PDIP stack-of-stars. (E) Maximum intensity projection from CTA focused to the pelvic vessels. [Note that the pelvic arteries were not included in the formal image analysis.] (F) Corresponding minimum intensity projection (b/w inverted) from PDIP stack-of-stars. There is excellent correspondence in the appearance of the vascular calcifications (arrows) in both regions. Bright signal in the corners of images (D) and (F) represent air-filled bowel loops.