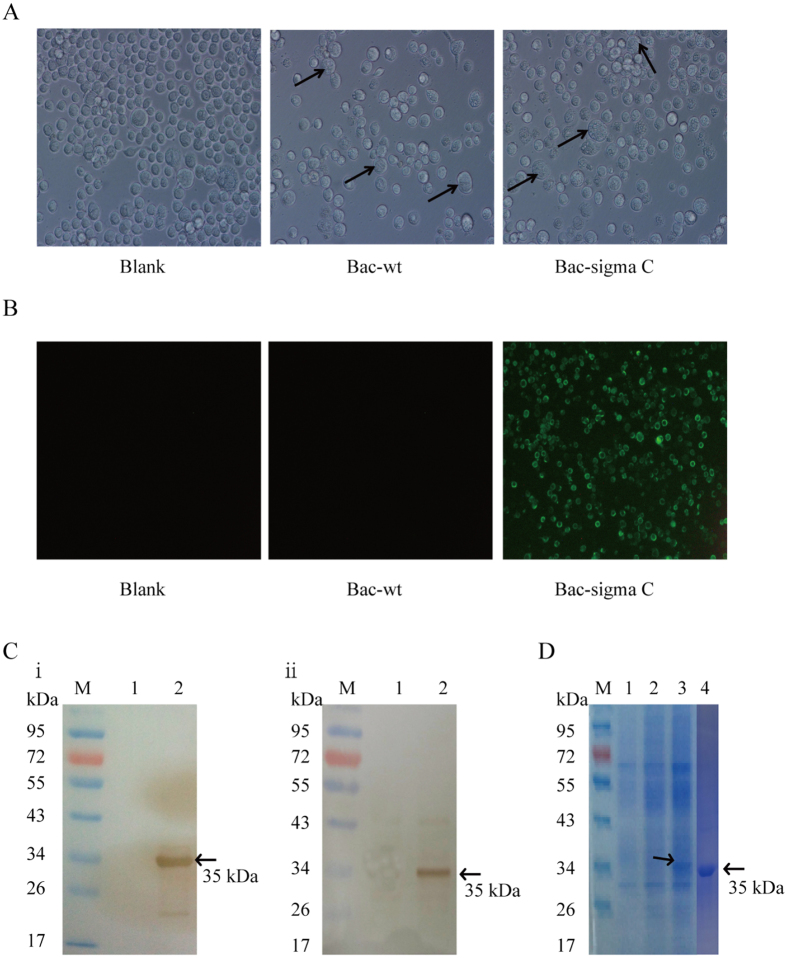
Figure 2. Identification and purification of recombinant sigma C protein.
(A) Characterization of baculovirus infected cells. Sf9 cells were infected with the recombinant sigma C baculovirus (Bac-sigma C), wild-type baculovirus (Bac-wt), and blank control (Blank). The arrows indicate larger cell size formation in Sf9 cells infected with Bac-wt and Bac-sigma C. (B) Immunofluorescence assay (IFA) of Bac-sigma C infected cells. After 48 h post-infection, cells were analyzed by IFA using the mouse antiserum of sigma C as primary antibody and FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG antibody as secondary antibody (original magnification, 100x). (C) Western blot analysis of recombinant sigma C protein in Bac-sigma C infected cells using anti-sigma C serum (i) and anti-His monoclonal antibody (ii). Lane M, molecular weight markers; Lane 1: Sf9 cells infected with Bac-wt; Lane 2: Sf9 cells infected with Bac-sigma C. (D) Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis of the purified sigma C fusion protein. Lane M, molecular weight markers; Lane 1: non-treated Sf9 cells; Lane 2: Sf9 cells infected with Bac-wt; Lane 3: Sf9 cells infected with Bac-sigma C; Lane 4: 2 μg purified sigma C protein.