Figure 4. Biogenetic profiles of extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscle fibre bundles under the basal condition and during FCCP‐induced maximal respiration.
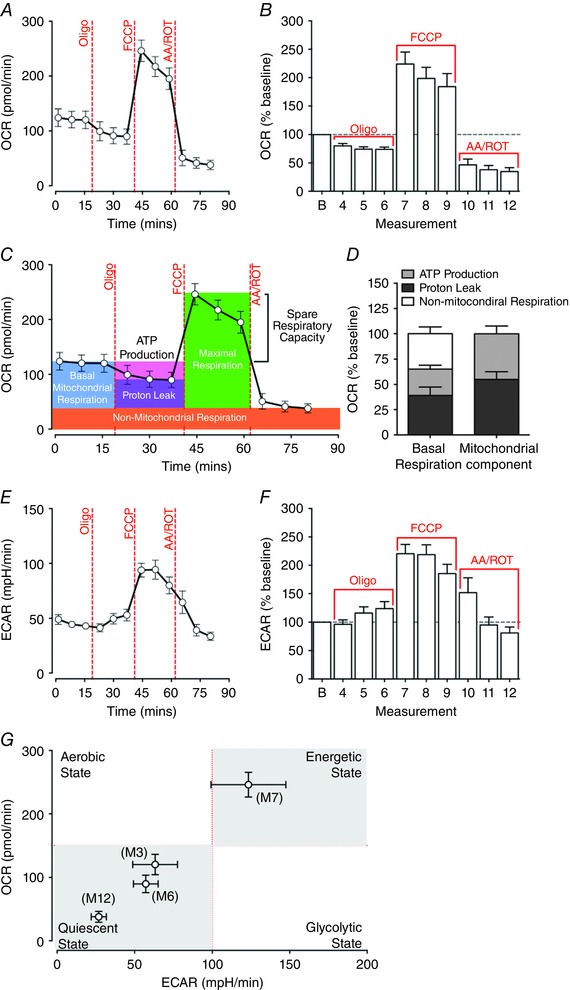
A and B, absolute values (A) and baseline normalised oxygen consumption rate (OCR; B) were determined in EDL fibre bundles at baseline and after FCCP‐induced maximal respiration. OCR levels were inhibited by oligomycin A to 73.94 ± 3.91% of the baseline at the sixth measurement cycle (M6) and surged to 224.05 ± 21.03% of the baseline at M7 following the injection of FCCP. C, key parameters of mitochondrial respiration in EDL fibre bundles determined by the mitochondrial stress assay. Oligomycin A inhibits ATP production‐related mitochondrial respiration, but does not prevent oxygen consumption through proton leak. Mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) complex I and III inhibitors antimycin and rotenone completely shut down mitochondrial oxygen consumption, leaving non‐mitochondrial‐related respiration. D, percentage proportions of ATP turnover, proton leak and non‐mitochondrial respiration contributed to total basal respiration and mitochondrial respiration in EDL fibre bundles. E and F, absolute values (E) and baseline normalised extracellular acidification rate (ECAR; F) from EDL fibre bundles. ECAR peaked at M7 following the injection of FCCP, accounting for 220.43 ± 16.36% of baseline respiration. G, matched OCRs and ECARs of EDL fibre bundles at the 3rd, 6th, 7th and 12th measurement, representing the energy phenotype at the basal state (M3) and after the exposure of oligomycin A (M6), FCCP (M7) and antimycin–rotenone (M12). The EDL fibre bundles switched to a high oxidative phosphorylation and high glycolysis phenotype under FCCP‐induced maximal respiration (n = 10). [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
