Figure 3. Reflex activation and KF stimulation: effects on CVBA.
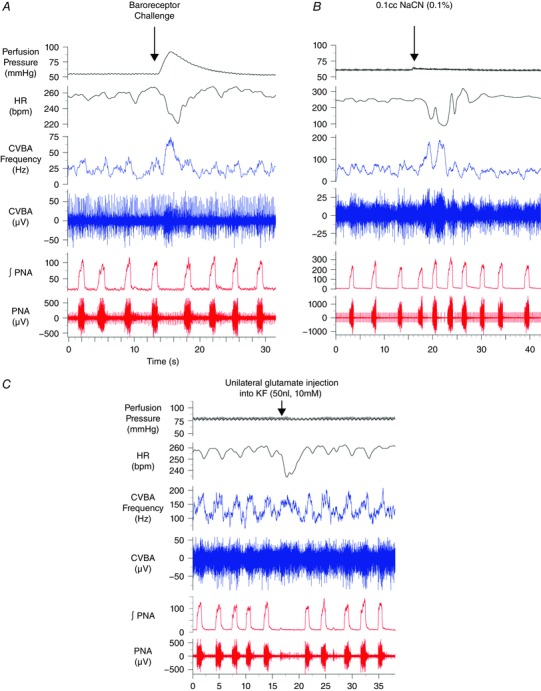
Representative traces from three separate experiments. Baroreceptor challenges, produced by a transient increase in the perfusion pressure (A), were associated with marked activation of the cardiac vagal branch and bradycardia. A bolus of sodium cyanide added to the perfusing solution (0.1 ml, 0.1%) evoked an increase in the magnitude and frequency of phrenic discharge and enhanced the firing rate of the cardiac vagal branch during post‐inspiration (B). These post‐inspiratory discharges were associated with periods of bradycardia. Unilateral microinjection of 10 mm glutamate into the KF prolonged the expiratory period (C). CVBA was maintained during the extended expiratory period, producing a bradycardia. ∫PNA, integrated phrenic nerve activity. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
