Figure 6. Inhibition of the KF reduces the magnitude of respiratory fluctuations in cardiac vagal activity and RSA.
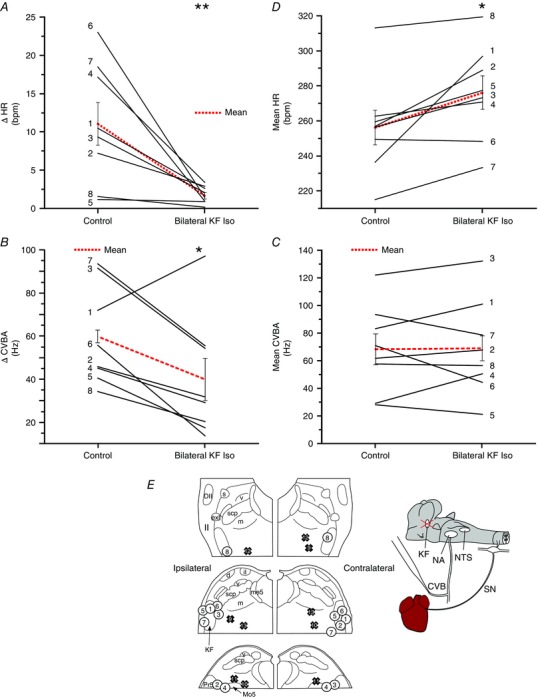
The magnitude of the RSA (ΔHR) (A) and of cyclical fluctuations in CVBA (ΔCVBA) (B) was reduced by bilateral injection of isoguvacine into the KF. Mean HR (C) showed an increase, whereas mean CVBA (D) was unchanged. Isoguvacine injection sites for each experiment are depicted in (E): numbered circles depict KF injections corresponding to numbered experiments in (A) to (D); numbered crosses depict control injections made 1 mm medial to KF (data not shown; see Results). ΔHR and ΔCVNA were calculated as the difference between the maximum and the minimum values over the course the single respiratory cycle. All parameters were averaged over ≥ 10 cycles/experiment. Data are values from individual experiments (black lines) and are the mean ± SEM (red dashed lines). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, paired t test (n = 8). il, internal lateral parabrachial nucleus; me5, mesencephalic trigeminal tract; Pr5, principal sensory trigeminal nucleus; scp, superior cerebellar peduncle m, medial parabrachial nucleus; s, superior lateral parabrachial nucleus; v, ventral lateral parabrachial nucleus. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
