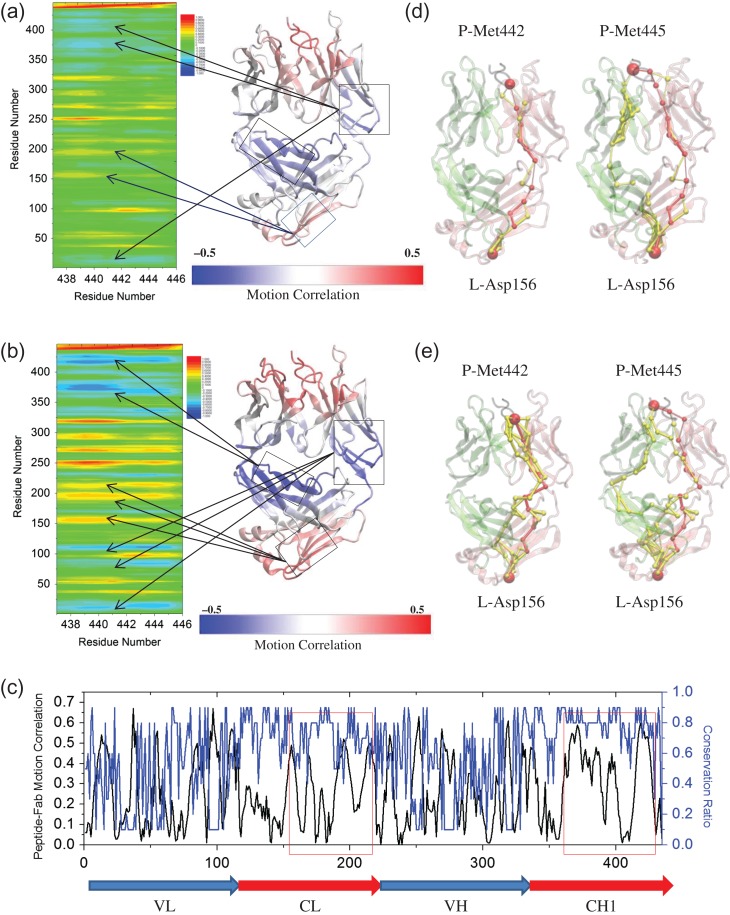
Fig. 4.
Distant motion correlation and allosteric signals between prion peptide and Fab controlled by the inter-chain disulfide bond. Correlation analysis (Cij) of the motion between two essential methionines of prion peptide and Fab in the complex system (a) with and (b) without the inter-chain disulfide bond during a 100-ns MD simulation. The averaged Cij is obtained by averaging the Cij values from Met442 and Met445. Residues with highly correlated motion to loosely correlated motion, and to highly anti-correlated motion are colored from red, green/yellow, to blue. The correlation of the motion between peptide and each individual Fab residue is mapped onto the Fab structure from highly correlated (red) to loosely correlated (white), and to highly anti-correlated (blue). (c) The absolute values of peptide–Fab motion correlation (black line) and conservation ratio (blue line, 0–0.9, higher value indicates higher conservation) of each individual residue of the bound system without inter-SS bond. Optimal and suboptimal paths connecting Met442/Met445 of prion peptide to Asp156 (d) with and (e) without the inter-chain disulfide bond. Optimal and suboptimal paths are colored by red and yellow, respectively. The thickness of each edge is proportional to the number of suboptimal paths that cross it during the calculation. Light chain, heavy chain and the peptide are colored by pink, lime and black, respectively. Met442/Met445 and Asp156 are represented by red beads.