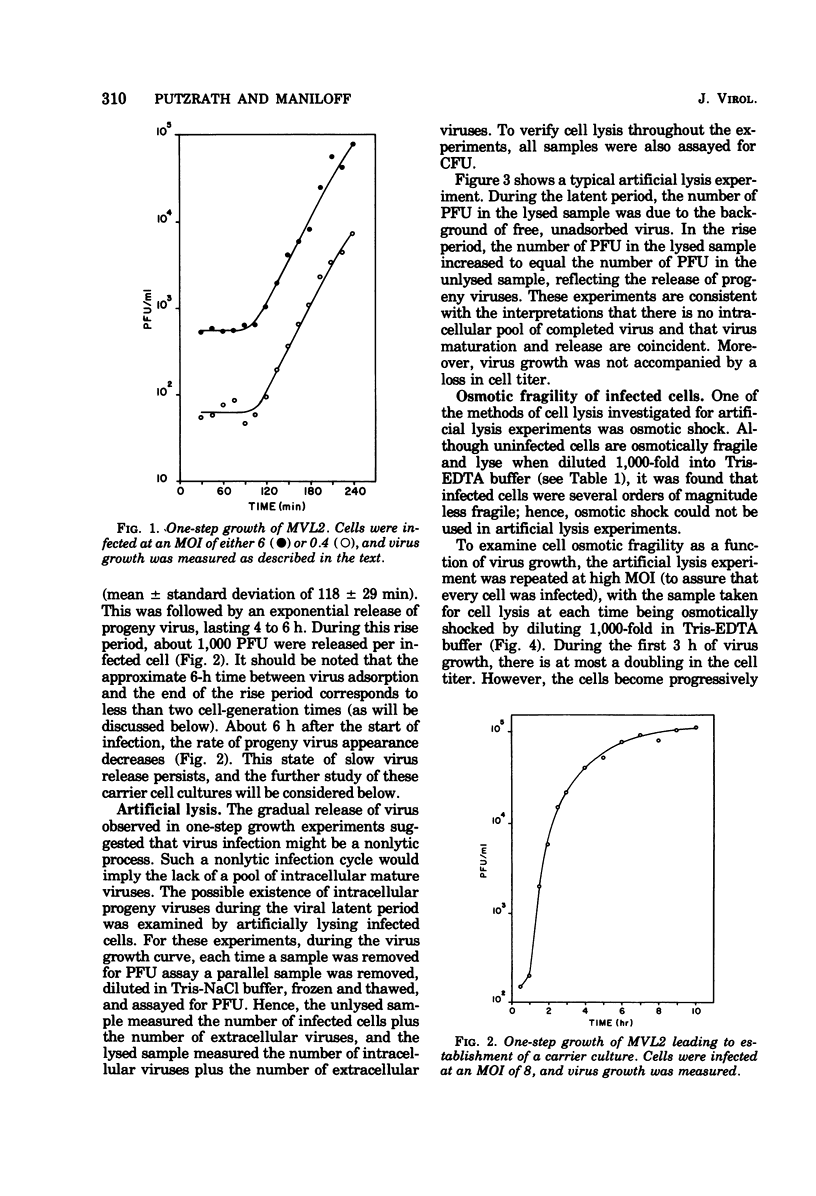
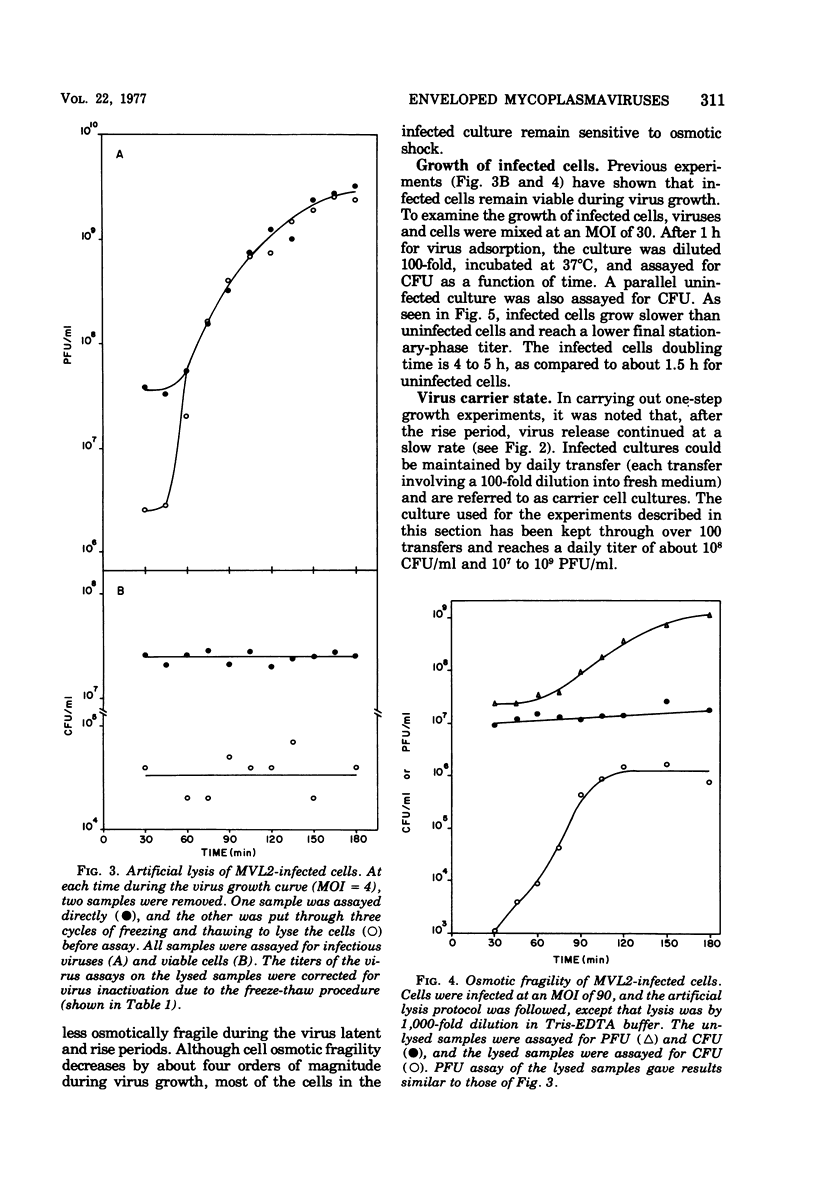
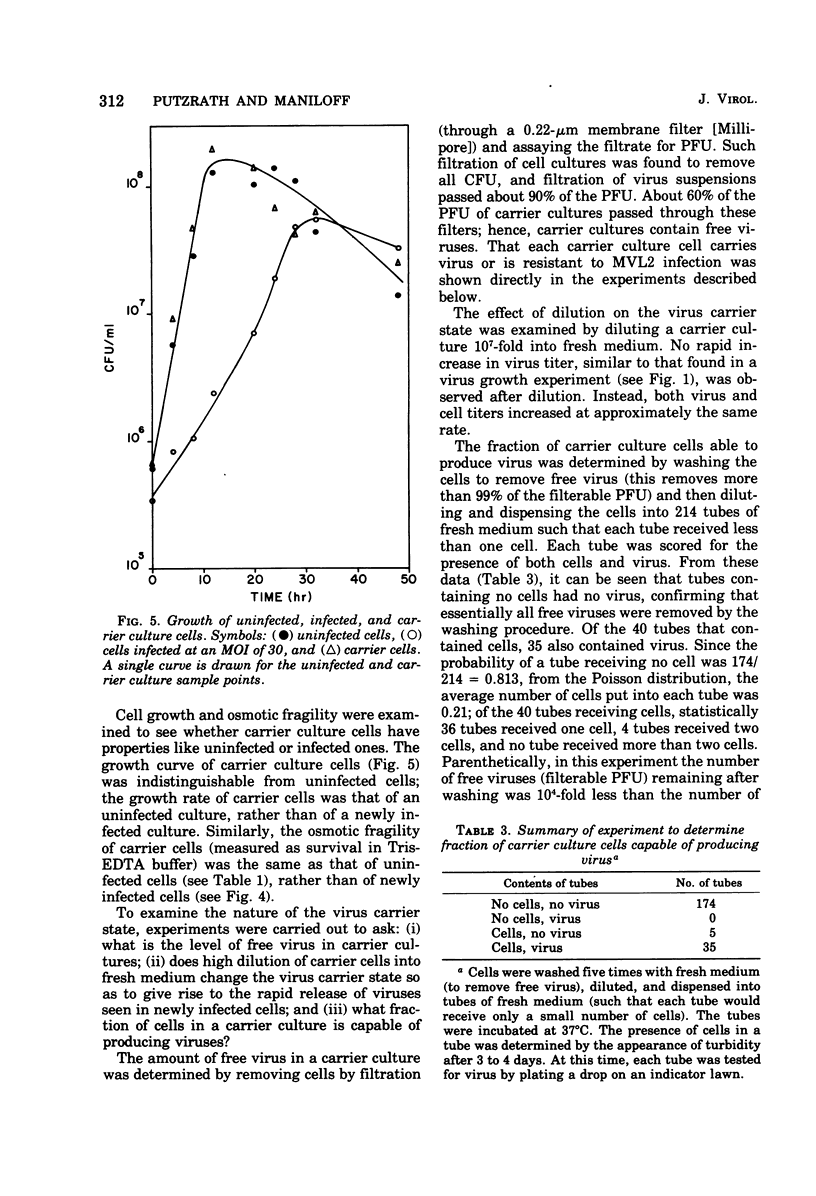
Abstract
The growth of an enveloped DNA-containing mycoplasmavirus (MVL2 obtained from R.N. Gourlay) has studied, by using the indicator host Acholeplasma laidlawii strain JA1. From virus one-step growth curves, artificial lysis experiments, and infected cell growth curves, it was found that virus infection is nonlytic. Newly infected cells grow slower and are osmotically more stable than uninfected cells. However, 4 to 6 h after infection, the cells reach a carrier state in which cell growth rate and osmotic fragility are indistinguishable from uninfected cells. Carrier cultures contain free virus. Every carrier culture cell gives rise to either a clone of carrier cells or a clone of MVL2-resistant cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carstensen E. L., Maniloff J., Einolf C. W., Jr Electrical properties and ultrastructure of Mycoplasma membranes. Biophys J. 1971 Jul;11(7):572–581. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86236-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M., Salditt M., Silbert J. A. Structure and synthesis of a lipid-containing bacteriophage. I. Growth of bacteriophage PM2 and alterations in nucleic acid metabolism in the infected cell. Virology. 1969 Aug;38(4):627–640. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N., Garwes D. J., Bruce J., Wyld S. G. Further studies on the morphology and composition of Mycoplasmatales virus-laidlawii 2. J Gen Virol. 1973 Feb;18(2):127–133. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-2-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N. Mycoplasmatales virus-laidlawii 2, a new virus isolated from Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Gen Virol. 1971 Jul;12(1):65–67. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-12-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liska B., Tkadlecek L. Electron-microscopic study of a Mycoplasmatales virus, strain MV-Lg-pS2-L 172. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1975;20(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF02877079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liss A., Maniloff J. Infection of Acholeplasma laidlawii by MVL51 virus. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liss A., Maniloff J. Isolation of Mycoplasmatales viruses and characterization of MVL1, MVL52, and MVG51. Science. 1971 Aug 20;173(3998):725–727. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3998.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvin D. A., Hohn B. Filamentous bacterial viruses. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):172–209. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.172-209.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan D. C., Liss A., Maniloff J. Eagle's basal medium as a defined medium for Mycoplasma studies. Microbios. 1972 Sep-Oct;6(22):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver A. K., Koski R. K., Van Etten J. L. Bacteriophage phi6: a Lipid-Containing Virus of Pseudomonas phaseolicola. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):799–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.799-805.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


