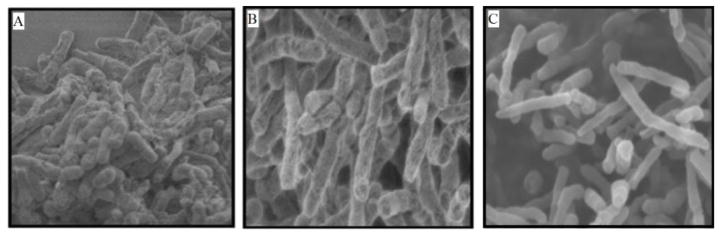
Figure 3.
(A) Normal cells divide and remain a short length. (B) and (C) Inhibition of FtsZ causes filamentation. Cells continue to grow and elongate, but cannot divide. Reprinted with permission from Huang, Q.; Kirikae, F.; Kirikae, T.; Pepe, A.; Amin, A.; Respicio, L.; Slayden, R. A.; Tonge, P. J.; Ojima, I., Targeting FtsZ for Antituberculosis Drug Discovery: Noncytotoxic Taxanes as Novel Antituberculosis Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49 (2), 463–466. Copyright 2012 American Chemical Society.