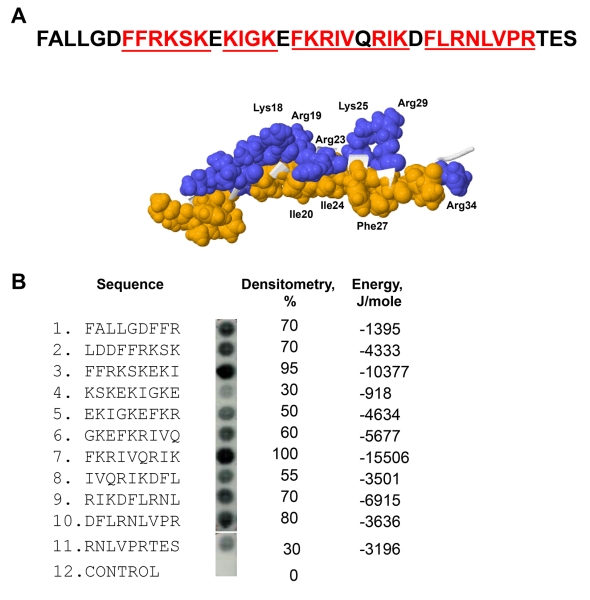
Figure 1. Characterization of the αMI-domain recognition motifs in the FALL-39 sequence.
(A) The amino acid sequence of FALL-39 and the 3D structure of LL-37 based on PDB Id: 2K6O. Positively charged (blue) and hydrophobic (tan) residues in the C-terminal part of the peptide are numbered. The underlined sequences denote the αMI-domain recognition patterns. (B) The peptide library derived from the FALL-39 sequence (left panel) consisting of 9-mer peptides with a 3 residue offset was incubated with 125I-labeled αMI-domain and the αMI-domain binding was visualized by autoradiography. Control, a spot containing only the β-Ala spacer used for the attachment of peptides to the cellulose membrane. The αMI-domain binding observed as dark spots was analyzed by densitometry (middle column). The numbers show the relative binding of the αMI-domain to peptides expressed as a percentage of the intensity of spot 3. The peptide energies (right column) that serve as a measure of probability each peptide can interact with the αMI-domain were calculated as described.20