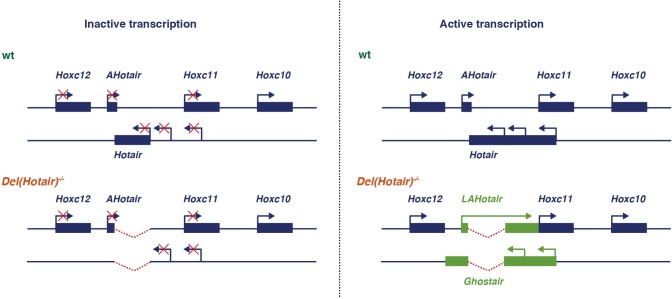
Fig 9. Schematic summarizing the data shown in Fig 8.
In a wild type situation and at a body level anterior to Hoxc11 expression (from example in the upper lumbar region such as L3 or L4), Hoxc10 is active whereas the whole posterior part of the HoxC cluster is repressed (top left). Once Hoxc11 and Hoxc12 become activated, in more posterior regions of the body, both the Hotair and the AntiHotair RNAs are produced, from the anti-Hox and Hox DNA strands, respectively (top, right). Upon deletion of the Hotair locus, the posterior HoxC cluster remains closed for transcription in the anterior parts of the body (bottom, left). In contrast, the activation of the Hoxc11 region (bottom right) triggers the transcription of Ghostair on the opposite DNA strand, which meets the 3’ end of the Hoxc12 transcription unit, perhaps causing the light decrease in Hoxc12 mRNAs. On the Hox strand, the anti-Hotair RNA can now cross over the deleted region and contribute to the transcription of Hoxc11, perhaps inducing the observed light gain of expression of the latter gene.