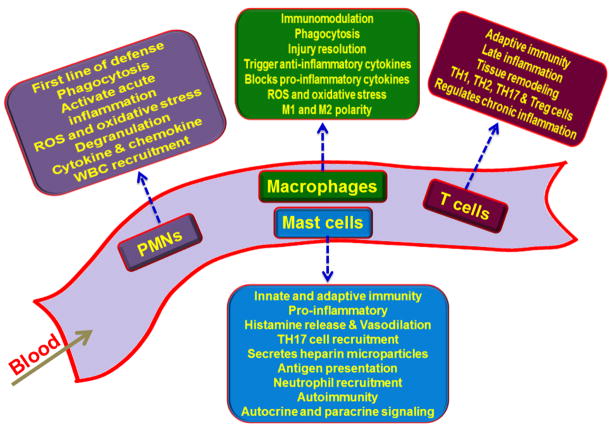
Figure 1. Specific role of immune cells in the progression and regulation of inflammatory responses.
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) are phagocytic cells associated with acute inflammation; macrophages have immunomodulatory effect owing to their phagocytic activity, cytokine release and repair responses; mast cells enhance inflammation due to histamine release and induction of vasodilation, and the T cells play role in tissue remodeling after injury.