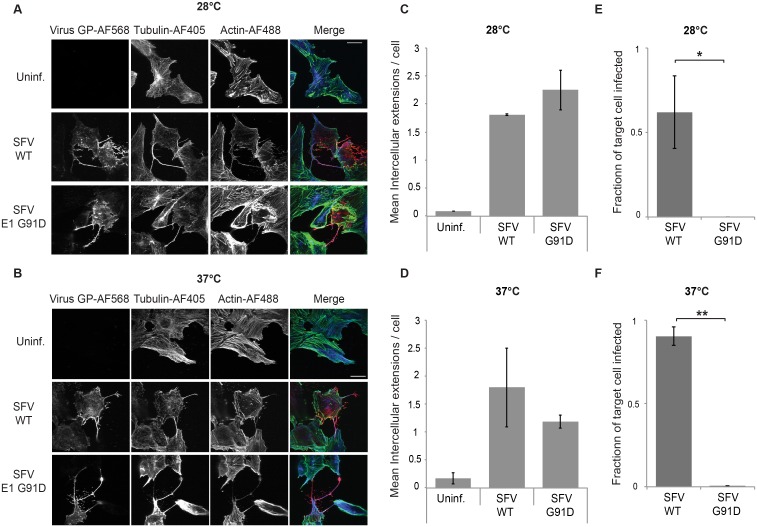
Fig 7. Formation of intercellular extensions does not require virus budding.
Vero cells were mock-transfected (Uninf.) or transfected with SFV WT or G91D mutant RNA, incubated at the permissive temperature (28°C) overnight (A) or at the non-permissive temperature (37°C) for 8 h (B), and fixed. Note that different times of incubation at these two temperatures were used to allow virus replication and extension formation. Cells were permeabilized and immunostained to detect the virus glycoproteins (GP) or α-tubulin, and stained with phalloidin-Alexa488 to detect F-actin. Cells were imaged by confocal microscopy. Images from one optical section are shown and are representative of the images from three independent experiments. Bar = 20 μm. (C,D) The number of intercellular extensions per infected cell (n = 10) was quantitated based on their positive staining for GP, actin and tubulin and their contact with a neighboring cell. (E,F) Vero cells were transfected with WT or G91D SFV RNA and incubated at 37°C for 2h (producer cells). At 4 h post-transfection Vero target cells stably expressing the PM-GFP marker were plated onto the infected cells at an approximate ratio of 1:1 and the co-cultures incubated overnight at 37 or 28°C. Cells were then fixed, permeabilized, and immunostained to detect the viral glycoproteins. Epifluorescence microscopy was used to acquire 5 images using the 20X objective. The number of infected PM-GFP-positive target cells was quantitated and expressed as a fraction of the total number of target cells. The graphs in C-F represent the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01.