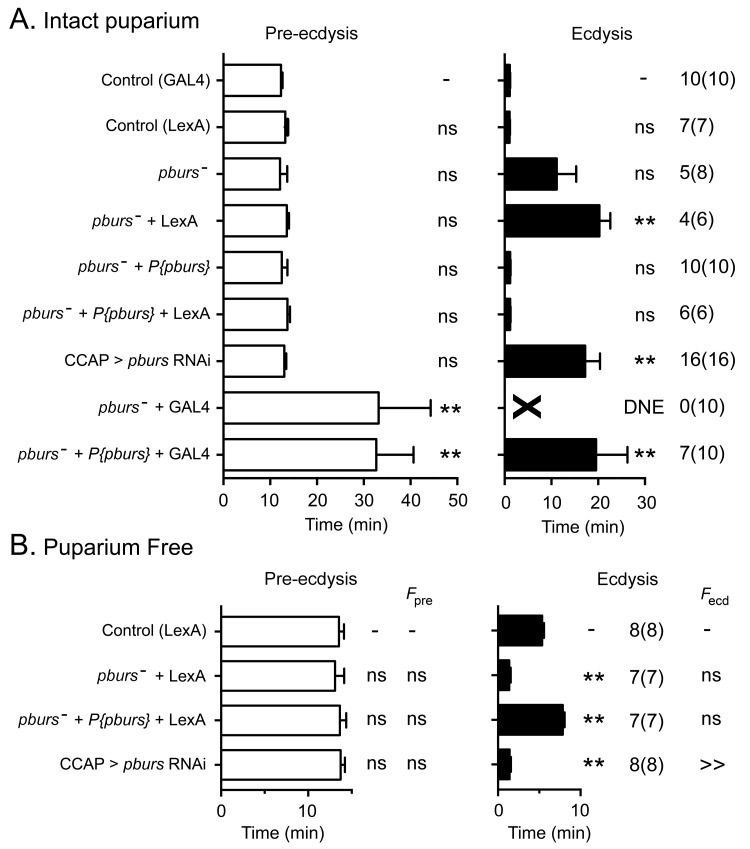
Figure 6. Ecdysial behaviors of pburs mutant animals.
(A,B) Duration of pre-ecdysis (left; open bars) and ecdysis (right; filled bars) behavior of animals hemizygous for pburs in intact (A) and in puparium-free preparations (B), shown as described in Figure 2. Data are mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA, Dunnett's post-hoc to control. Actual p values can be found in Supplementary file 1. Lack of pburs function did not significantly alter the duration of the pre-edysis phase (unless CCAP neurons also expressed GAL4, see below), whereas it lengthened (intact preparations) or shortened (puparium free preparations) the duration of ecdysis; a similar result was obtained when pburs function was knocked down using RNAi. In (A), note that expression of GAL4 in CCAP neurons accentuated the defects expressed by pburs hemizygotes; these defects could not be rescued by pburs-containing transgene and were therefore not caused only by the lack of pburs function. For this reason, GCaMP responses to ETH of pburs mutants were assessed using Ccap-LexA driver (cf., Figure 7). Genotypes: Control (GAL4): CCAP-GAL4+UAS-GCaMP; Control (LexA): CCAP-LexA+LexAop-GCaMP. All genotypes including '(GAL4)' or ('LexA') contained CCAP-GAL4+UAS-GCaMP or CCAP-LexA+LexAop-GCaMP, respectively. pburs[-]: pburs[-]/Df(2)pburs; pburs[-]+P{pburs}: pburs[-]/Df(2)pburs; P{pburs}; see Materials and methods for exact genotypes. In all experiments using RNAi, its effectiveness was boosted by including a UAS-dcr2 transgene.