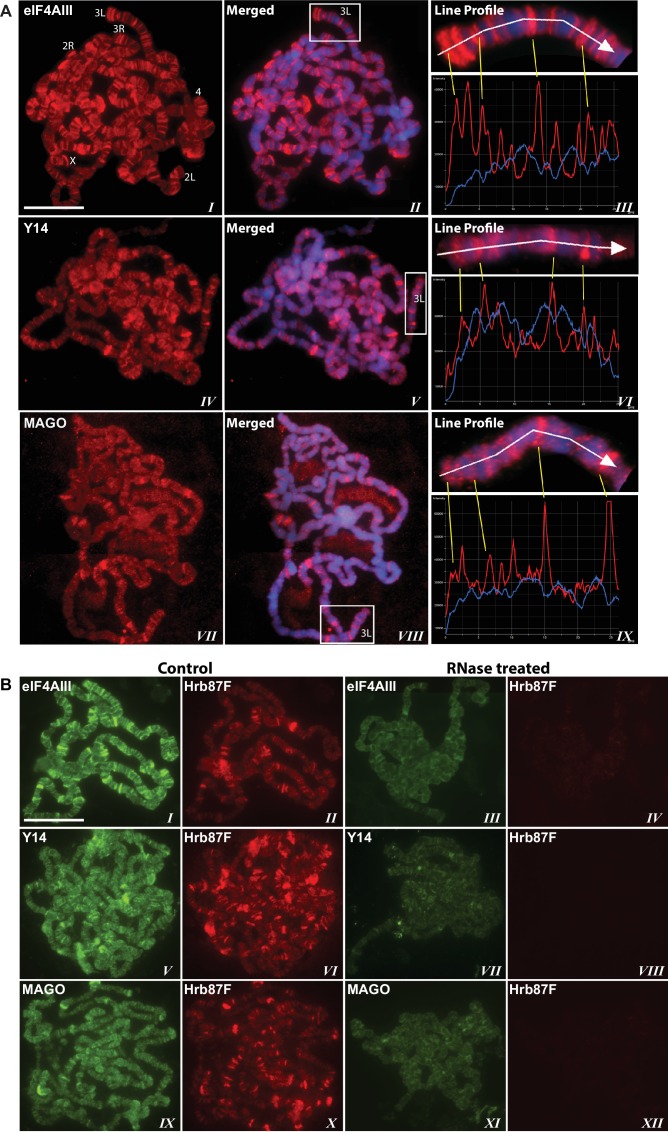
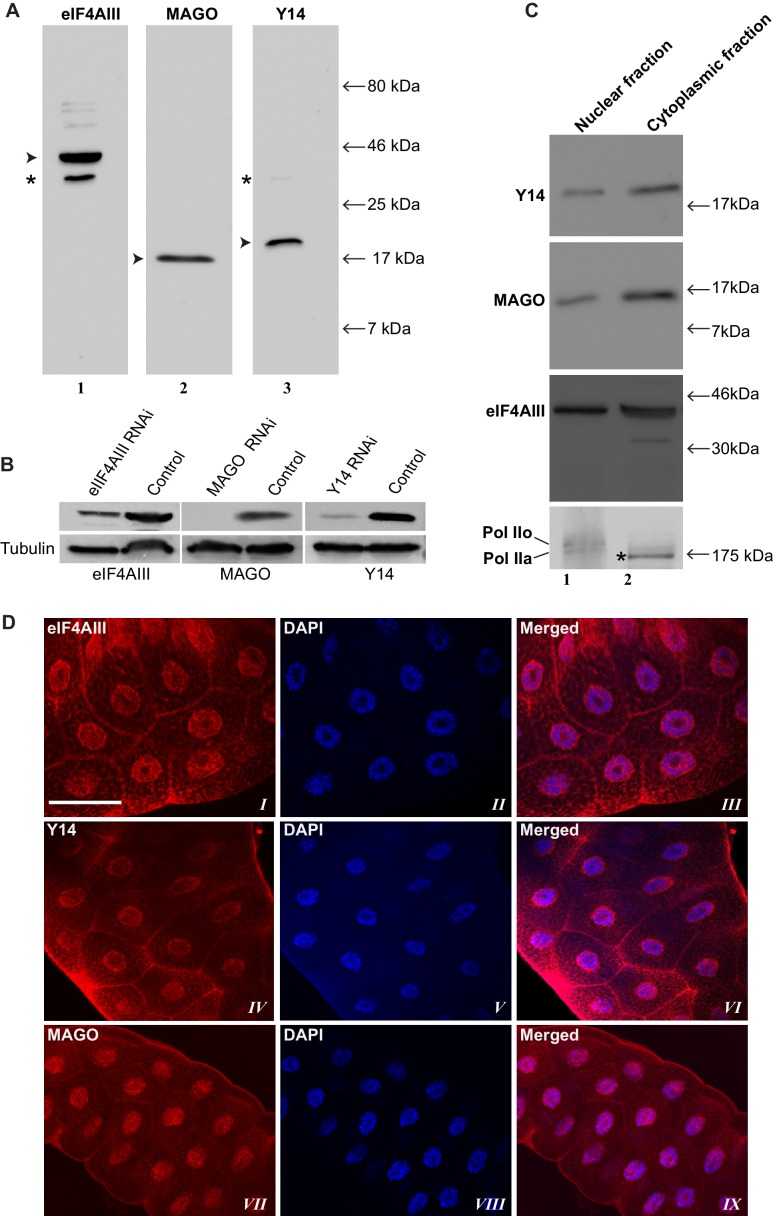
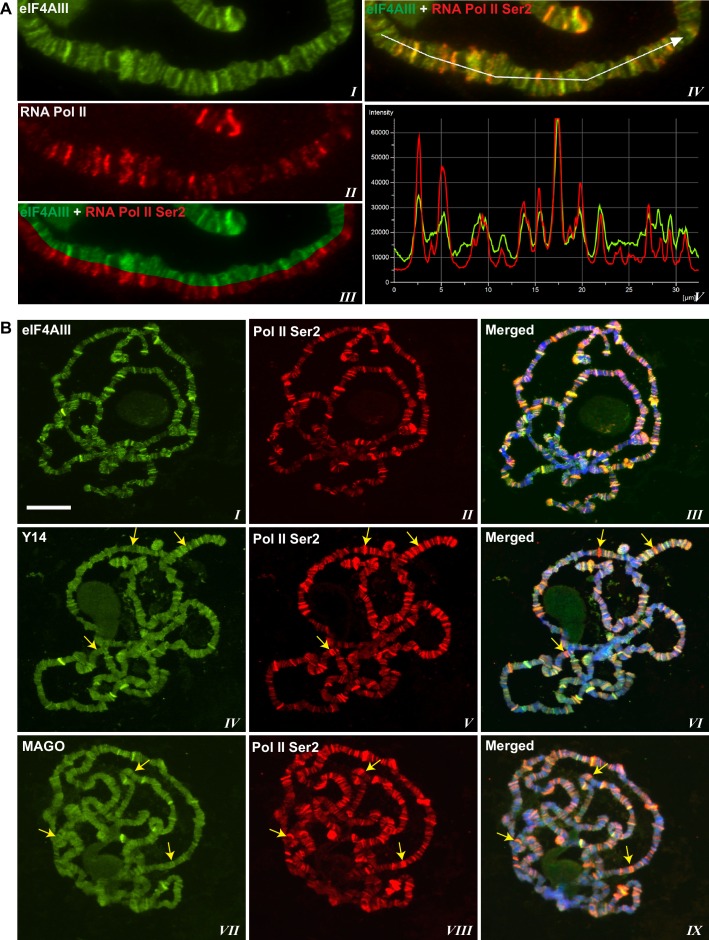
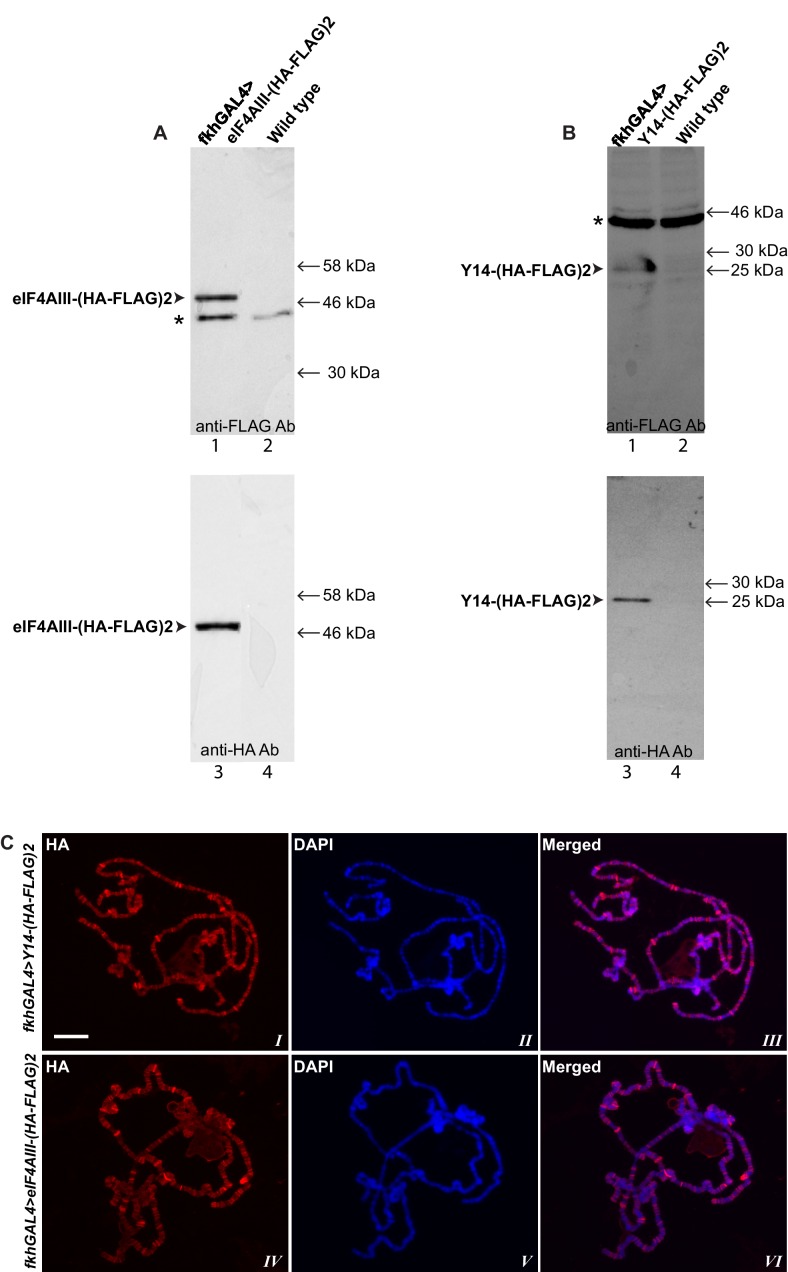
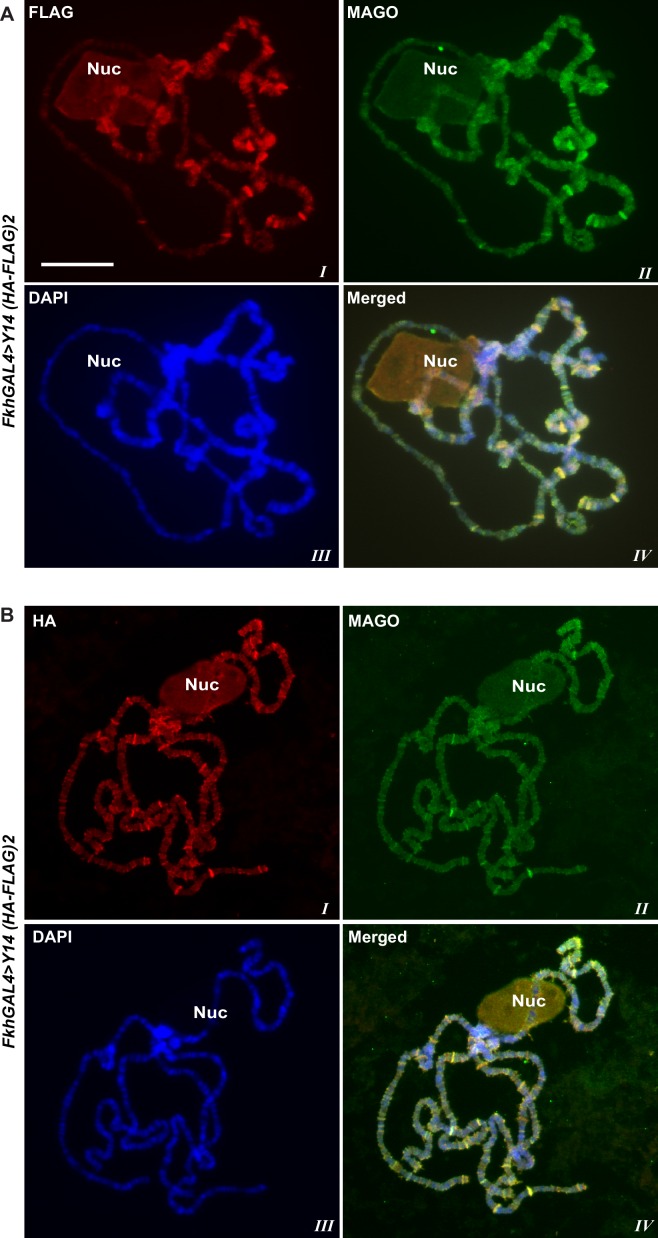
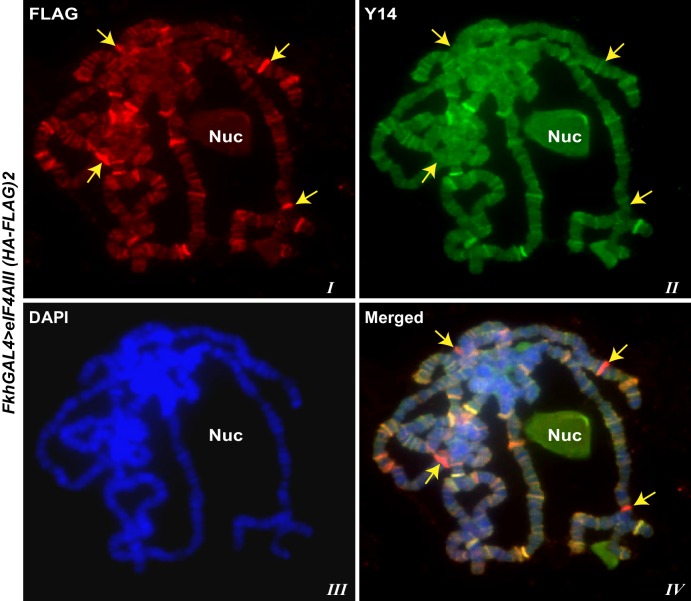
Figure 1. The EJC core proteins associate with nascent transcripts at polytene chromosomes.
(A) Immunolocalization of EJC proteins (red), eIF4AIII (I-III), Y14 (IV-VI) and MAGO (VII-IX), on salivary gland polytene chromosomes of wandering third instar larvae. Chromosomes were counter-stained with DAPI (blue). Intensity profiles of EJC protein and DAPI signals (III, VI, IX) over a segment at the tip of chromosome 3L (box in merged images) show accumulation of these proteins at interband regions. Scale bar represents 20 µm length. (B) Parallel immunolocalization of EJC proteins (green) and Hrb87F (hnRNP A1) (red) on polytene chromosomes spread from salivary gland without treatment (Control) or after incubation with RNase (RNase treated). Scale bar represent 20 µm length.