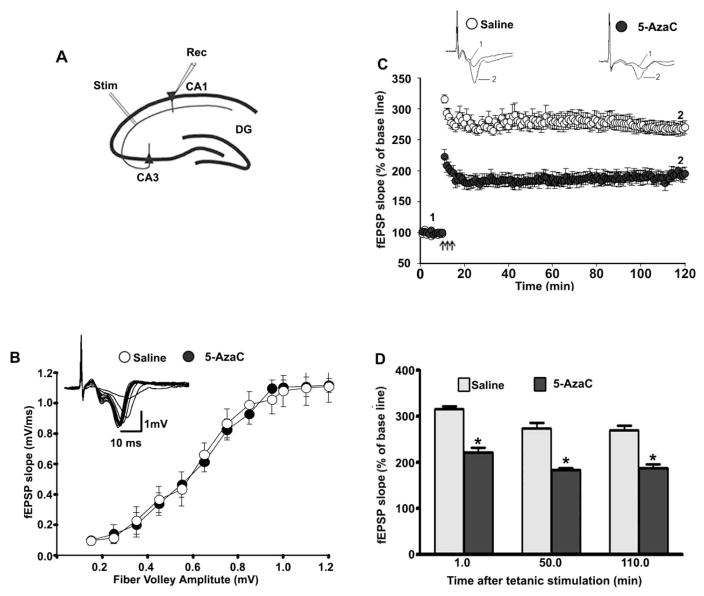
Fig. 8.
Exposure of P7 mice to 5-AzaC induces LTP deficits in adult mice. (A) A schematic drawing showing the positions of the stimulating and recording electrodes in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. (B) A summary graph showing the field input/output relationships for the P7 saline- and 5-AzaC-treated adult mice. Insert: An example of traces taken from representative experiments showing the input/output relationships for the saline group. Although it is not shown, the other groups also exhibited comparable patterns. (C) The time course of the average fEPSP slope obtained from the P7 saline- and 5-AzaC-treated adult mice. The fEPSP slopes from each LTP recording were normalized to the mean value of 10 min recordings obtained before stimulation. The arrows indicate the time of TBS (4 pulses at 100 Hz, with bursts repeated at 5 Hz, and each tetanus including 3 different 10-burst trains separated by 15 s). Representative traces of the fEPSPs before (trace 1) and after (trace 2) the induction of LTP in hippocampal slices from P7 saline- and 5-AzaC-treated adult mice. (C) A combined plot of the average of the fEPSP slopes at several time points. Error bars, SEM (n = 5 mice/group; 10 slices/group). *p < 0.01 vs. saline.