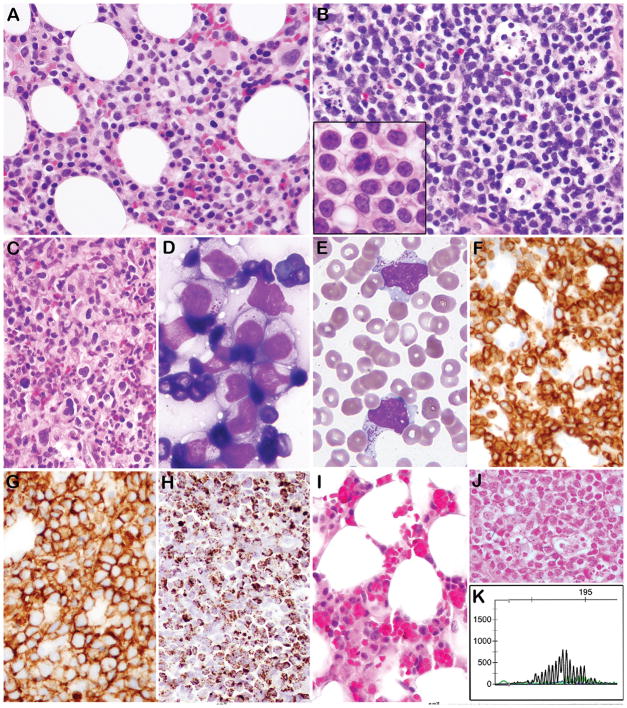
Figure 1. Morphological, immunophenotypic, and genotypic features of EBV negative ANKL.
A. Bone marrow biopsy contains atypical interstitial infiltrate composed of medium sized lymphocytes with fine chromatin and abundant pale cytoplasm (Case 3). B. A lymph node is diffusely infiltrated by atypical lymphocytes with abundant apoptotic debris in tingible body macrophages. The tumor cells on touch prep were medium in size with round/irregular nuclei, pale cytoplasm and easily identifiable mitoses (B, inset) (Case 5). C. The bone marrow from Case 4 contains more pleomorphic lymphocytes ranging in cell size, with reactive histiocytes in the background. D. A touch prep from an omental mass showed cytologically atypical lymphocytes with pale cytoplasm containing prominent azurophilic granules (Case 3). E. Circulating cells with prominent azurophilic granules are present (Case 5). By Immunohistochemistry the cells express cytoplasmic CD3 (F), CD56 (G), and Granzyme B (H). I. Bone marrow (Case 2) shows reduced hematopoiesis and numerous histiocytes with hemophagocytosis. J. All cases were negative for EBER by ISH (Case 3) K. PCR for TCRG showed a polyclonal rearrangement pattern (Case 5).