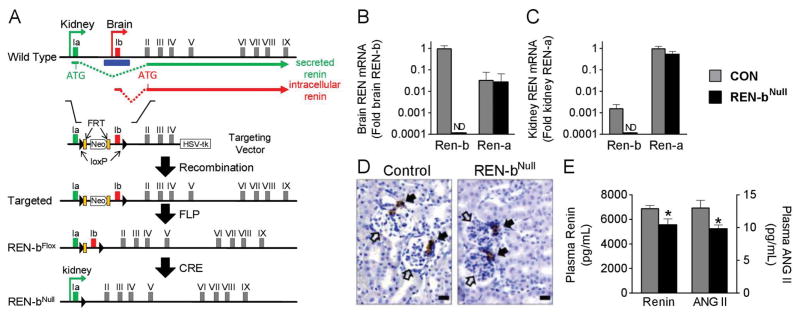
Figure 1. Generation of Renin-bNull Mice.
(A) Strategy for generating renin-bNull mice. The locations of exon 1a (green) and exon 1b (red) along with FRT (orange block) and loxP (black triangle) sites are indicated. The location of isoform-specific translation start sites and splice sites to exon II are indicated. Homologous recombinant founder mice containing the targeted allele were bred with FLPase mice to generate the floxed allele. The null allele was then generated by breeding with EIIA-Cre transgenic mice. Exon 1a and the common portions (exon 2 to 9) of the renin gene were retained in the Ren-bNull allele to preserve renin-a expression. (B–C) Renin-b and renin-a mRNA expression were measured in brain (B) and kidney (C) by real-time quantitative RT-PCR analysis (n=5 per group). ND, not detected. Graphs are mean±SEM. (D) Immunohistochemistry for renin in the kidney. Scale bars: 10 μm. Open arrow head, glomerulus; closed arrowhead, juxtaglomerular apparatus. (E) Plasma renin and angiotensin peptide levels were measure by ELISA (n=5 per group). *, P<0.05 vs control.