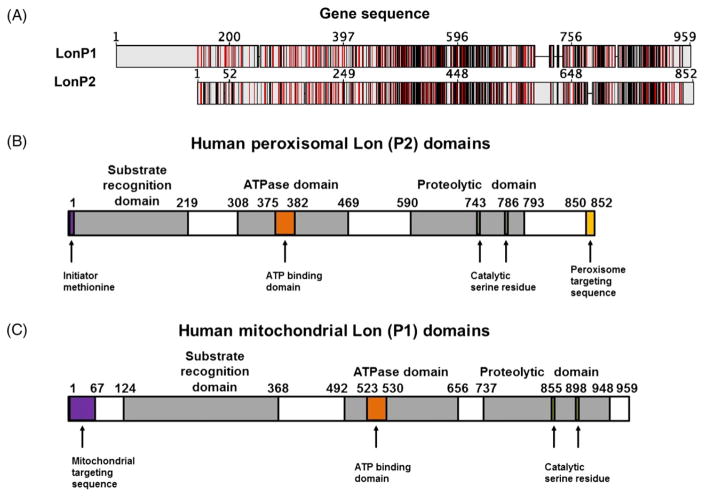
Fig. 2.
Peroxisomal and mitochondrial Lon protease. (A) The sequence alignment between the mitochondrial (LonP1) and peroxisomal (LonP2) forms of Lon. Identical sequences are shown in red and similar sequences are shown in grey. (B, C) Conserved domains of the P2 peroxisome-specific (B) and P1 mitochondrion-specific (C) isoforms of Lon. Both LonP1 and LonP2 contain a substrate recognition, ‘N’ domain to bind oxidized proteins. Both isoforms possess a classical ATPase domain containing Walker (A) and (B) motifs that have a characteristic tertiary structure commonly found in ATP-binding proteins. Lastly, both contain a proteolytic domain that relies upon a catalytically active serine residue for substrate degradation. However, unlike LonP1, which has a mitochondrial targeting sequence on the N-terminus, LonP2 relies upon the peroxisomal targeting sequence, which consists of a conserved three amino acid SRL motif.