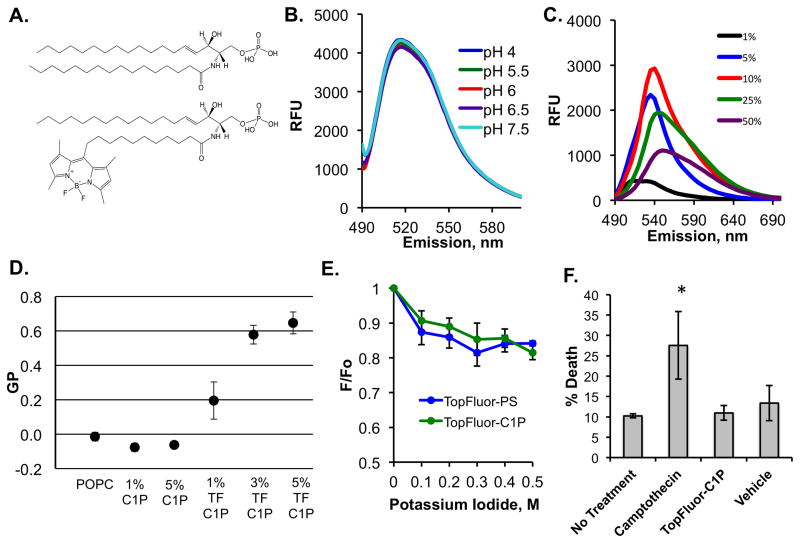
Figure 1. Biophysical Properties of TopFluor-C1P.
A) The structures of C1P (d18:0/16:0) (top) and TopFluor-C1P (bottom), which harbors a dipyrromethene boron difluoride (TopFluor) moiety at the tail end of the amine-linked acyl chain, are shown in their fully protonated state. B) The emission spectra (excitation at 470 nm and emission 490–600 nm) of 100 nm liposomes containing 1% TopFluor-C1P and 99% POPC at varying physiological pH values are shown. RFU = relative fluorescence unit. C) Increasing mol% of TopFluor-C1P was incorporated into POPC vesicles and the emission spectra (490–600 nm) was collected following excitation at 470 nm. D) The general polarization (GP) values from a laurdan assay containing MLVs with the indicated lipid concentrations in POPC. GP was measured using the equation, GP = (I435 − I480)/(I435 + I480). MLVs were excited at 340 nm and the emission was measured from 390 to 600 nm. E) A potassium iodide quenching assay was performed for liposomes containing either 1 mol% TopFluor-C1P or 1 mol% TopFluor-PS in DOPC vesicles. The emission (510 nm) was collected following excitation at 470 nm and the data were plotted as a ratio of (F/F0) versus the concentration of potassium iodide. F0 = fluorescence before KI addition, F = fluorescence after KI addition. F) Flow cytometry using the dye 7-AAD was employed to assess cell death for A549 cells treated with nothing, camptothecin, TopFluor-C1P or vehicle control. * p < 0.05. TF = TopFluor.