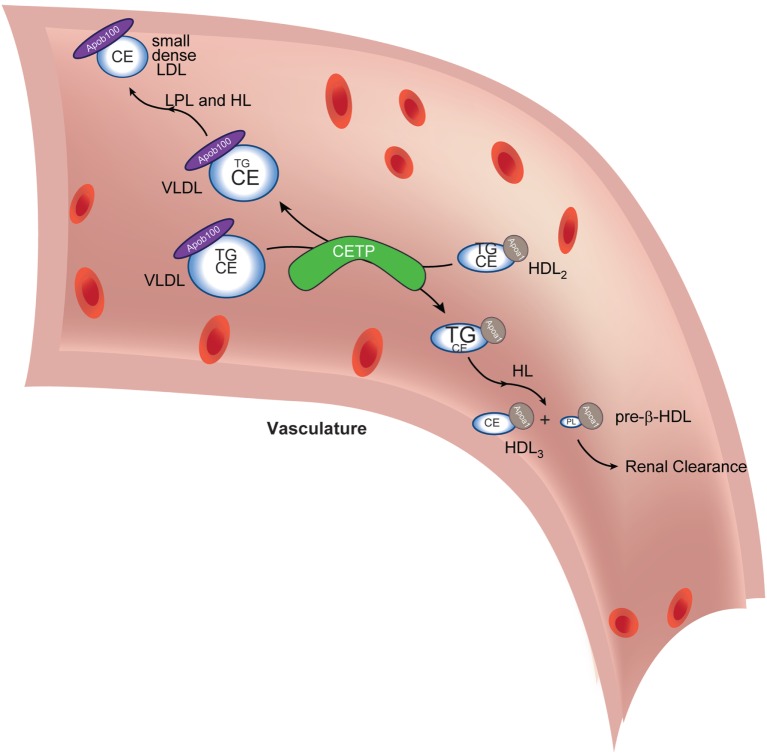
Figure 2.
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) in lipoprotein lipid exchange. Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles and HDL2 exchange triacylglycerol (TG) and cholesteryl esters (CE) in a reaction catalyzed by CETP. The depletion of TG and increase in VLDL CE (reflected in altered font sizes) coupled with lipoprotein lipase (LPL)- and hepatic lipase (HL)-mediated (further) depletion of TG (not shown) lead to the formation of small dense low-density lipoprotein (LDL), which is amenable to oxidative modification, a conversion central to driving subsequent atheromatous plaque formation. The transient increase in TG in HDL2 (reflected in increased font size) delivers a substrate for HL-mediated hydrolysis (as it passes through the liver capillaries). This reaction generates small HDL3 and pre-β-HDL, which contain scant amounts of phospholipids only. Pre-β-HDL is removed from the circulation via renal filtration. The net effect of CETP action, thus, is to cause maturation of VLDL into atherogenic, small, dense LDL and to decrease atheroprotective HDL concentration. Apoa1 is the signature coat protein of HDL.