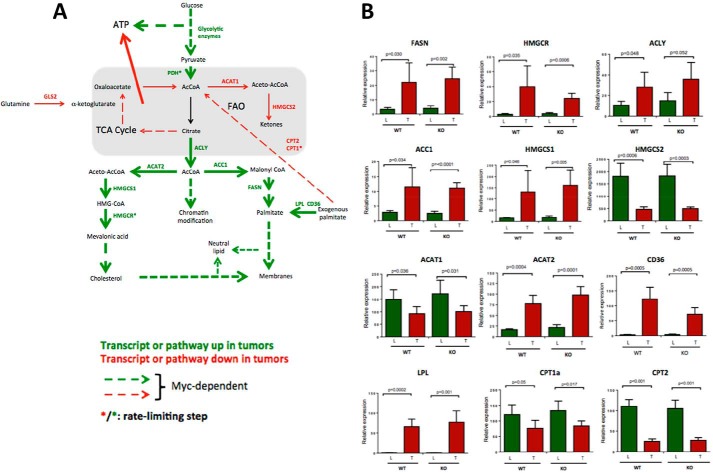
FIGURE 5.
Myc-dependent and Myc-independent pathways in HB tumorigenesis. A, summary of relevant tumor pathways and targets. ATP generated by the up-regulation of glycolysis in tumors is sufficient to offset the overall loss of ATP generated by reduced Oxphos. B, relevant levels of expression in hepatocytes and HBs of the transcripts encoding the enzymes depicted in A. Data were taken from the results shown in Fig. 4 and supplemental Fig. S9. Error bars indicate ± S.E. The abbreviations used are: FASN, fatty acid synthase; HMGCR, HMG-coenzyme A reductase; ACLY, ATP citrate lyase; ACC1, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; HMGCS1 & 2, HMG-coenzyme S synthase, cytoplasmic and mitochondrial, respectively; ACAT1&2, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase: mitochondrial and cytoplasmic, respectively; CD36, receptor for thrombospondin, oxidized low density lipoprotein, oxidized phospholipids, long-chain fatty acids, and native lipoproteins; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; CPT1a, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A; CPT2, carnitine palmitoyltransferase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase.