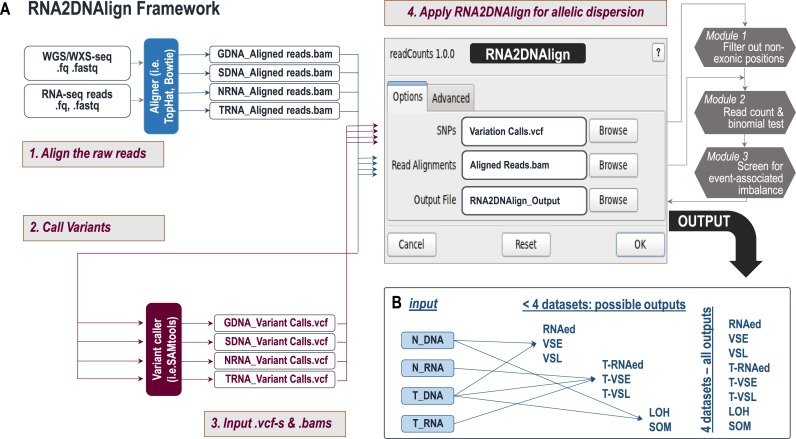
Figure 2.
(A) RNA2DNAlign workflow. RNA2DNAlign uses generated variant call files (.vcf) and binary alignments (.bam) derived from matching RNA and/or DNA sequencing datasets. Upon filtering of exonic positions (Module 1) the algorithm accesses each alignment file (Module 2) to read the counts and compute the likelihoods for all the possible genotypes (DNA) and allelic statuses (RNA). Module 3 then screens for significant genotypes and allelic statuses and compares them between the matching datasets to outline variants associated with any type of imbalance. (B) Relationship between input and output datasets. To assess for allele distribution matching an events, RNA2DNAlign requires a minimum of two datasets. SOM and LOH can be extracted from normal and tumor exomes; RNAed, VSE and VSL, can be assessed through comparisons between normal exomes and transcriptomes, and T-RNAed, T-VSE and T-VSL can be assessed through alignment of the tumor exomes to the normal and tumor transcriptomes. When all 4 datasets are available, RNA2DNAlign generates all 8 outcomes; otherwise it produces only the possible outcomes.