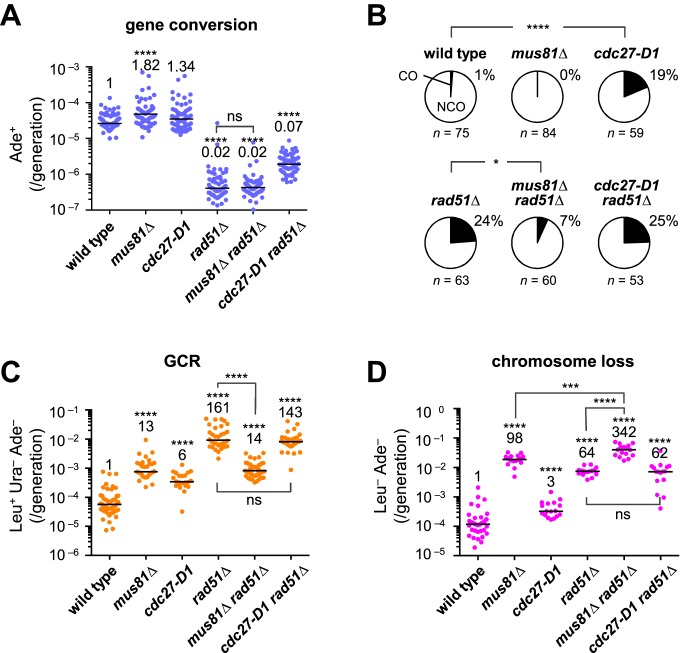
Figure 6.
Mus81 is required for COs and GCRs in the rad51Δ mutant. (A) Rates of spontaneous gene conversion in the centromere and (B) proportion of COs among Ade+ recombinants were determined using wild-type, mus81Δ, cdc27-D1, rad51Δ, mus81Δ rad51Δ and cdc27-D1 rad51Δ strains (TNF3144, 6035, 6312, 3257, 6234 and 6335, respectively). Spontaneous rates of (C) GCRs and (D) chromosome loss were determined using wild-type, mus81Δ, cdc27-D1, rad51Δ, mus81Δ rad51Δ, and cdc27-D1 rad51Δ strains (TNF5369, 5669, 5402, 5411, 5974 and 5671, respectively) that contain ChLC minichromosome. Only the position of the ura4+ marker differs between ChLC and ChL: 10 and 170 kb from irc3R, respectively. Because the rate of chromosome loss was too high to obtain sufficient GCR clones to determine GCR rates in the mus81Δ rad51Δ mutant, GCR rates were determined using cells grown in EMM+UA media to pre-select the cells that retained the minichromosome (see Materials and Methods). Pre-selection can, at least in part, explain why the GCR rate of rad51Δ was relatively higher (161-fold increase) than that shown in Figure 1B (85-fold increase), where cells were grown in YE+LUA rather than EMM+UA. In Figure 1B, the GCR rate of the mutants that lost minichromosomes at a high rate such as rad51Δ may be slightly underestimated, as the cells that did not retain the minichromosome were included in the total count. ns, P > 0.05.