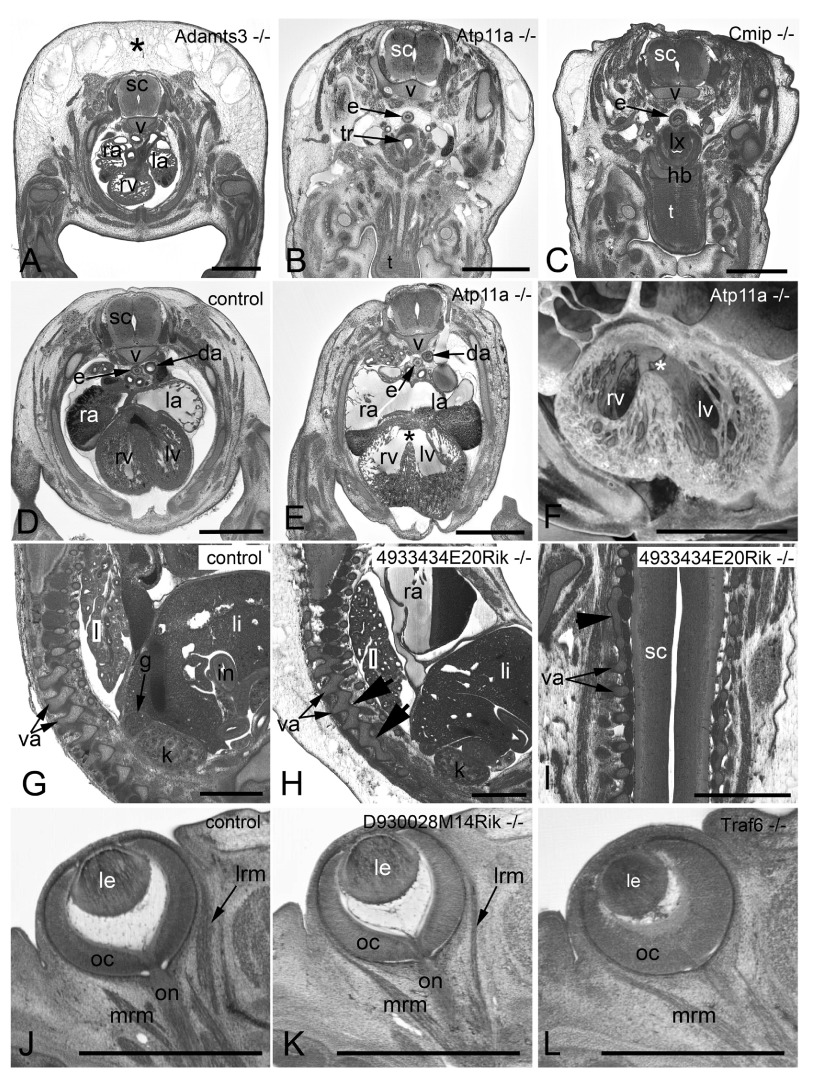
Figure 3. Examples of frequently observed abnormalities.
A– C. Subcutaneous edema. Original HREM sections showing a massive (asterisk) ( A), mild ( B), and unilaterally located subcutaneous edema ( C). Note the shrinkage artefacts in B and C, which complicate post mortem diagnosis. D– F. Perimembraneous septal defect. Normal situation in a control ( D) as appearing in an original HREM section. Defect (asterisk) as appearing in an original HREM section ( E) and a 3D volume model ( F). G– I. Fusion of vertebral arches. Normal situation in a control ( G) as appearing in a sagittal section. Fused articular processes (arrowheads) of subsequent vertebrae in a sagittal ( H) and a coronal section ( I). J– L. Abnormal eye muscle morphology as appearing in original HREM sections. Normal situation in a control ( J). Thinning of the lateral rectus muscle (lrm) ( K). Absence of the lateral rectus muscle (lrm) ( L). da, descending aorta; e, esophagus; g, adrenal gland; hb, hyoid bone; i, intestine; k, kidney; l, lung; la, left atrium; le, lens; li, liver; lrm, lateral rectus muscle; lv, left ventricle; lx, larynx; mrm, medial rectus muscle; oc, optic cup; on, optic nerve; ra, right atrium; rv, right ventricle; sc, spinal chord; t, tongue; tr, trachea; v, body of vertebra; va, arch of vertebra. Scale bars: 1 mm.