Figure 2.
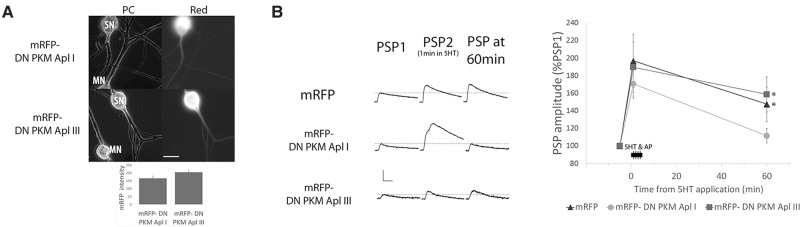
PKM Apl I is required for activity-dependent ITF. (A) Images of sensory (SN) to motor neuron (MN) pairs in phase contrast (PC) and with mRFP fluorescence filters (Red) showing mRFP tagged PKM expression in the sensory neuron (scale bar is 40 µm). Inset, bar graph showing the average mRFP intensity in mRFP-DN PKM Apl I and mRFP-DN PKM Apl III groups used in the experiment. mRFP intensity measured in the SN soma and expressed as a fold increase above the average autofluorescence intensity observed in SN somata. There is no significant difference between the mRFP intensity in the two groups (P > 0.05 Student's unpaired t-test). (B) PSP amplitude 60 min after evoking 20 action potentials at 10 Hz in the sensory neuron at 1, 2, 3, and 4 min of a 5 min 5HT application. Representative traces of PSPs from each group before 5HT application (PSP1), the first PSP produced from the stimulation during 5HT (PSP2) and the PSP 60 min after 5HT application (PSP 60 min). Scale bars are 5–5–2.5 mV/15 msec. PSP amplitude was significantly increased at 60 min with mRFP alone or mRFP-DN PKM Apl III, but not with mRFP-DN PKM Apl I expression in the sensory neuron (comparing before to 60 min following 5HT and sensory neuron activity with a paired Student's t-test, n = 13, 12, and 11 synaptic connections in each group), (*) P < 0.05 after Bonferroni correction for multiple t-tests. An ANOVA of the normalized PSP amplitudes gave a value of (F(33,2) = 2.35, P = 0.112. Initial PSP amplitudes were 21.3 ± 3.9, 27.8 ± 5.5, 23.8 ± 6.3 mV; initial MN input resistances were 64.1 ± 5.3, 72.4 ± 6.4, 67.8 ± 3.7 MΩ; and the changes in input resistance at 60 min as 98.8%, 90.7%, 88.5% of initial in mRFP, mRFP-DN PKM Apl I, and mRFP-DN PKM Apl III, respectively. There were no significant differences between the groups for any of these parameters (P > 0.05 ANOVA).