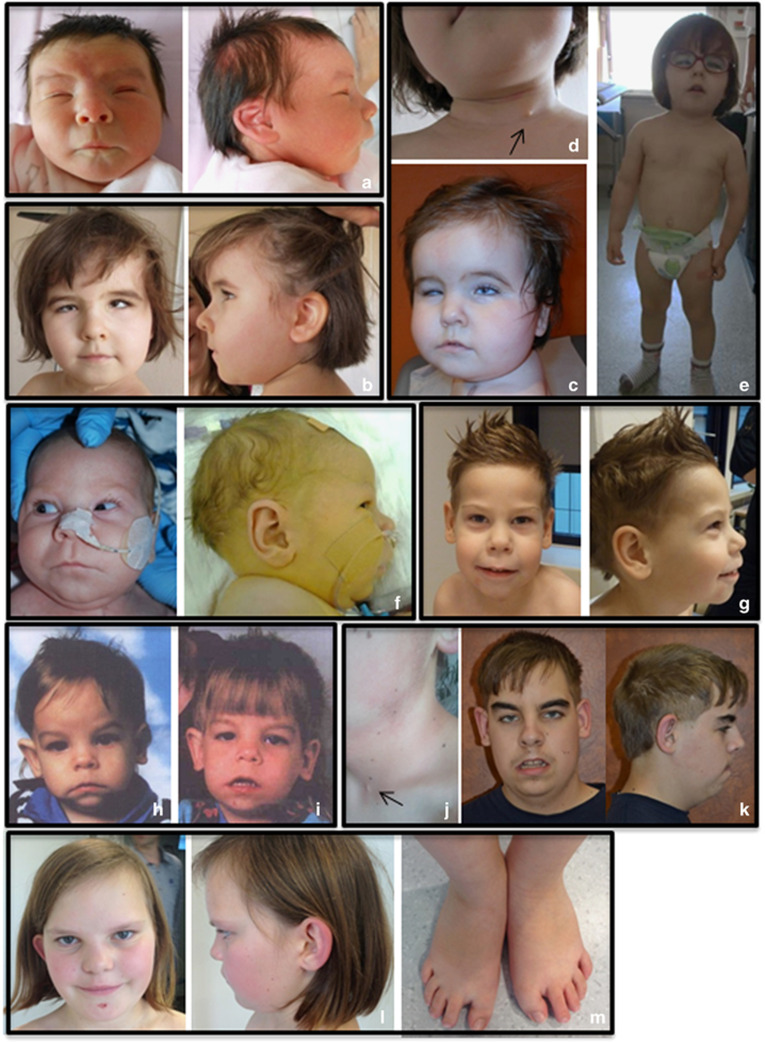
Figure 1.
Facial characteristics of the individuals with PUF60 variants. (a–c) Frontal and lateral views of patient 1 at birth (a) at 3 years and 3 months (b) and at 1 year (c) demonstrating facial dysmorphism including a square face, full cheeks, prominent forehead with bitemporal narrowing, low-set eyebrows, asymmetric and posterior rotated ears, bilateral colobomatous microphtalmia with horizontal nystagmus and convergent strabismus, bilateral epicanthal folds, wide nasal bridge with broad nasal tip and anteverted nares, thin upper lip with a long philtrum, micrognathism and broad short neck. (d) Lateral view of the neck of patient 1 showing a branchial cleft cyst (arrow). (e) Full-body view of patient 1 showing the contrast between the normal head circumference and the low body height and weight with relatively short arms, and a pectus excavatum. (f, g) Frontal and lateral views of patient 3 at birth (f) and at 3 years and 10 months (g) showing an elongated face, bilateral epicanthal folds, short up-slanted palpebral fissures, long eyelashes, anteverted nares, long prominent philtrum, thin upper lip and a short neck. (h–k) Frontal and lateral views of patient 4 at the age of 8 months (h), 2 years (i) and 17 years (k). (j) Lateral view of the neck of patient 4 showing a branchial cleft cyst (arrow). (l, m) Frontal and lateral view of patient 5 at the age of 11 years (l) showing deep set eyes, broad nasal bridge with protruding ears. (m) Flat feet with short halluces and sandal-gap deformity.