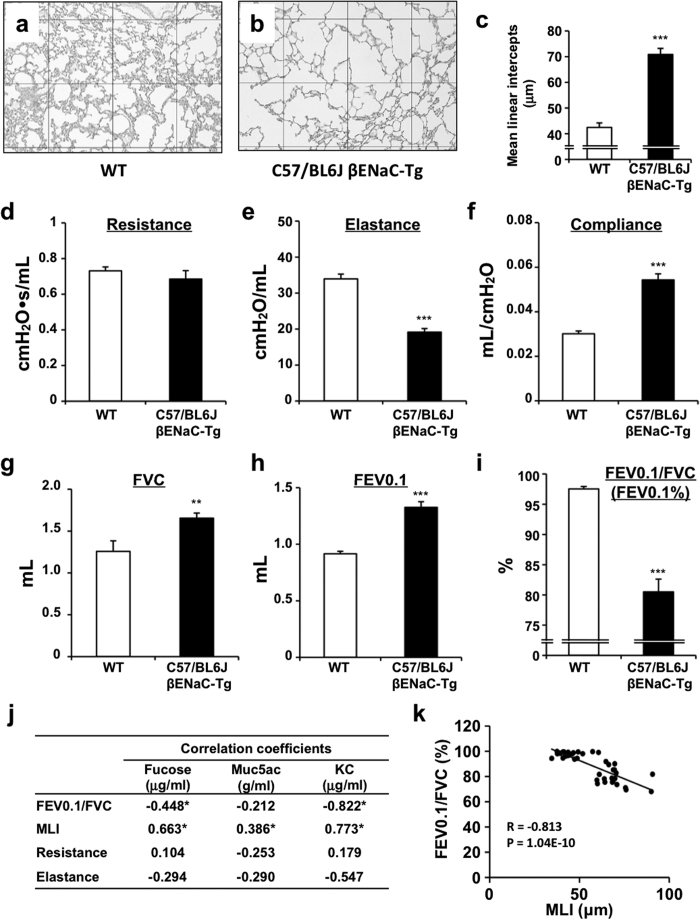
Figure 2. Pulmonary emphysema and dysfunction C57/BL6J-βENaC-Tg mice.
(a–c) Emphysematous phenotypes of WT and C57/BL6J-βENaC-Tg mice. Representative data of PAS and alcian blue-stained section of WT (a) (n = 9) and C57/BL6J-βENaC-Tg (b) (n = 11) mice. Square diameter, 300 μm. Quantitative morphometric analysis of alveolar septae of the lungs is shown in (c). (d–i) Respiratory parameters (resistance, elastance, compaliance, FVC, FEV0.1 and FEV0.1%) of WT (n = 15) and C57/BL6J-βENaC-Tg (n = 17) mice analyzed by flexiVent. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, versus WT; Student’s t test. (j,k) Correlation analysis of parameters. Summary of analysis between pulmonary parameters and biochemical parameters in BALF in WT and C57/BL6J-βENaC-Tg mice (n = 36–41) (j). *p < 0.05; Pearson’s correlation coefficient test. Correlation scatter plots of MLI and FEV0.1% (k).