Figure 3.
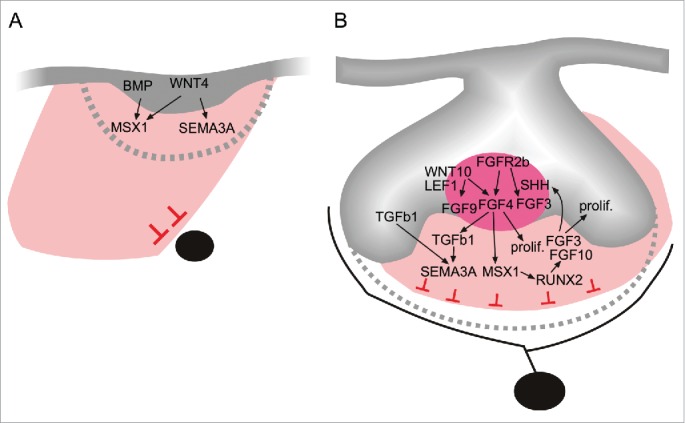
A model showing select signaling pathways and networks involved in the coordination of tooth morphogenesis and innervation during initiation (A), and the early morphogenetic cap stage (B). Tooth formation is crucially dependent on epithelial-mesenchymal interactions, which also regulate mesenchymal Sema3A, and the subsequent timing and patterning of tooth target innervation. Members of the conserved FGF (FGF4), Wnt (WNT4), and TGF-β superfamily (TGFß1) regulate SEMA3A expression. These signaling pathways are part of a larger odontogenic signaling network involving genes that are absolutely necessary for tooth formation in man and mouse, such as the MSX1 transcription factor.23,24,66-68,69,70,71
