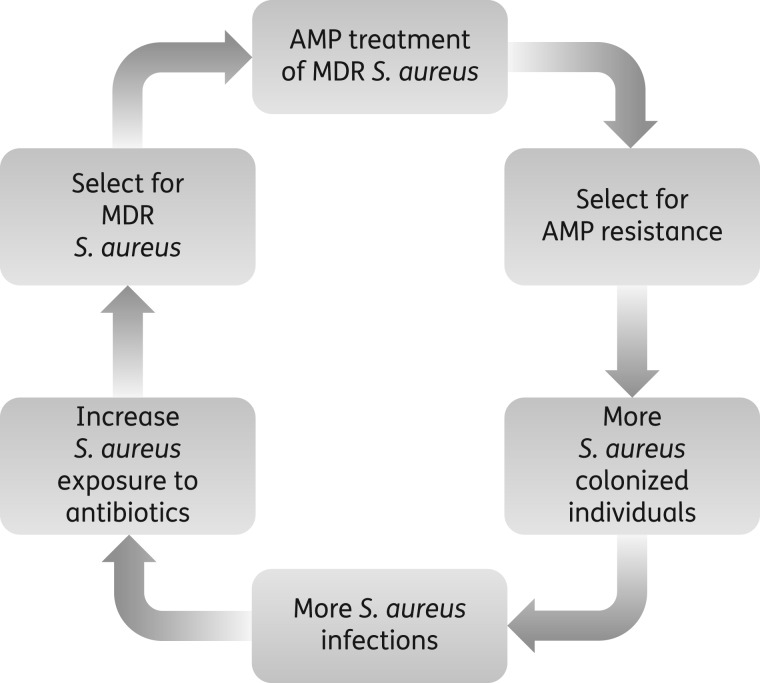
Figure 5.
Possible consequences of clinical AMP usage. Widespread clinical use of host-derived AMPs to treat MDR S. aureus may cause a vicious cycle further limiting treatment options. Continuous exposure to host-derived AMPs results in a stable AMP-resistant phenotype with reduced susceptibility to human defence peptides allowing for enhanced colonization of humans. Persistently colonized individuals are more susceptible to invasive S. aureus infections, which require antibiotic treatment. However, AMP-resistant S. aureus is associated with decreased susceptibility to antibiotics thereby increasing the use of last resort drugs. Enhanced exposure to these antibiotics will increase pressure for the evolution of bacterial resistance yielding highly drug-resistant pathogens.